Mitsubishi Eclipse. Technical Information Manual (1994) - part 36
POWER TRAIN
Manual Transaxle
Detent
ball (3)
Hub
Sleeve
Stop ring Speed gear Sleeve
stop ring
Gear
teeth
6
Spring
Gear cone
Sleeve
contacts
gear teeth
Full gear
engagement
Stop ring is pushed
into gear cone
045-050
Gear
0475-045
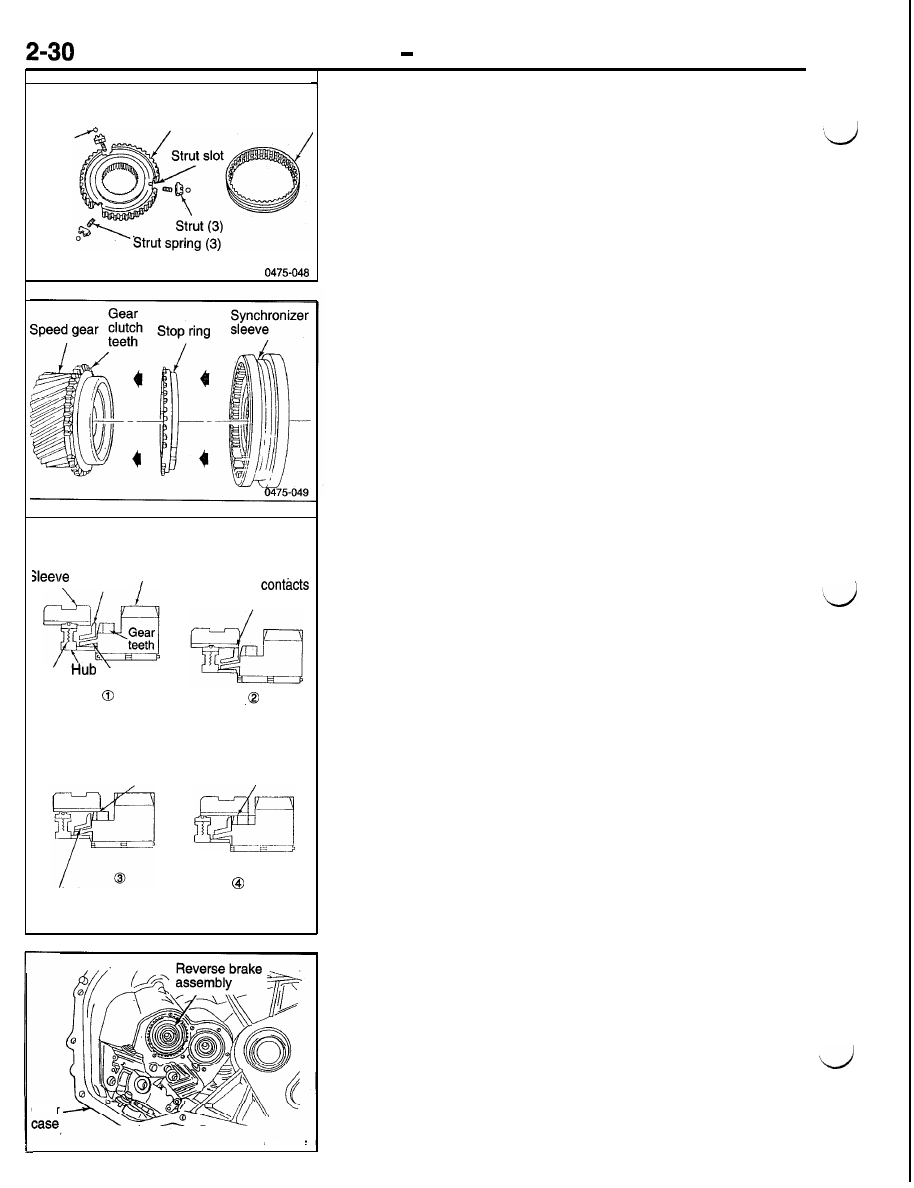
SYNCHRONIZER COMPONENTS
The synchronizer assemblies contain a sleeve, hub, struts,
springs and detent balls. The sleeve has inner splines that
slide on the hub and an outer radial slot that engages the
shift fork. The hub has inner splines that engage the shafts
and outer splines that the sleeve rides on. The outer hub splines
have three slots, cut lengthwise, for the struts.
Stop rings are located between the synchronizer and the speed
gears. The stop ring acts as a clutch to bring both the shaft
and speed gear to the same speed, without gear clash. During
a shift, the sleeve slides on the hub and over the stop ring
to engage the gear clutch teeth. When the sleeve and the
stop ring touch, they immediately begin to equalize speeds,
or synchronize.
The balls are held against the sleeve by the synchronizer
springs. The struts slide in the hub slots during a shift. The
synchronizer springs use a detent ball to center the strut in
the synchronizer sleeve. Before the sleeve and stop ring contact
each other, the struts engage lugs on the stop ring, pushing
the stop ring onto the gear cone. The sleeve teeth then block
against the stop ring teeth until the gears synchronize. The
slots in the hub are slightly larger than the lugs on the stop
ring allowing the ring to turn when it contacts the gear. The
turning of the stop ring is often referred to as “clocking.”
REVERSE BRAKE
A reverse brake assembly is used to stop input shaft rotation
through a friction cone which is locked to the transaxle case.
The brake is located in the rear case behind the input shaft
5-R synchronizer. The brake prevents the reverse idler gear
from clashing with the input and output shaft gears.