Frelander 2. Manual - part 128
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
Description and Operation
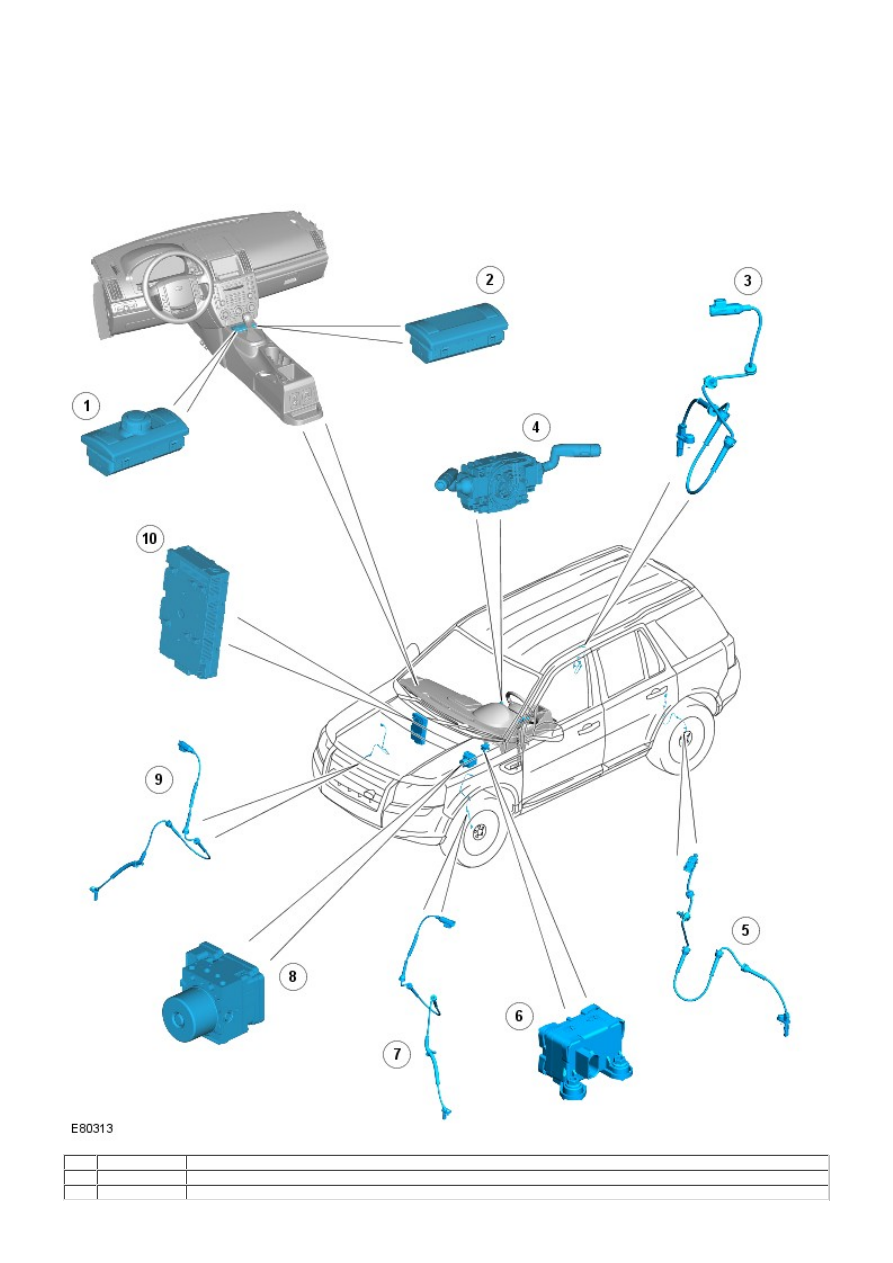
COMPONENT LOCATION
• NOTE: Left-Hand Drive (LHD) shown; Right-Hand Drive (RHD) similar.
Item Part Number
Description
1
-
Hill Descent Control (HDC) and Dynamic Stability Control (DSC) switches (with Terrain Response™)
2
-
HDC and DSC switches (without Terrain Response™)