Saturn Ion (2007 year). Manual - part 21
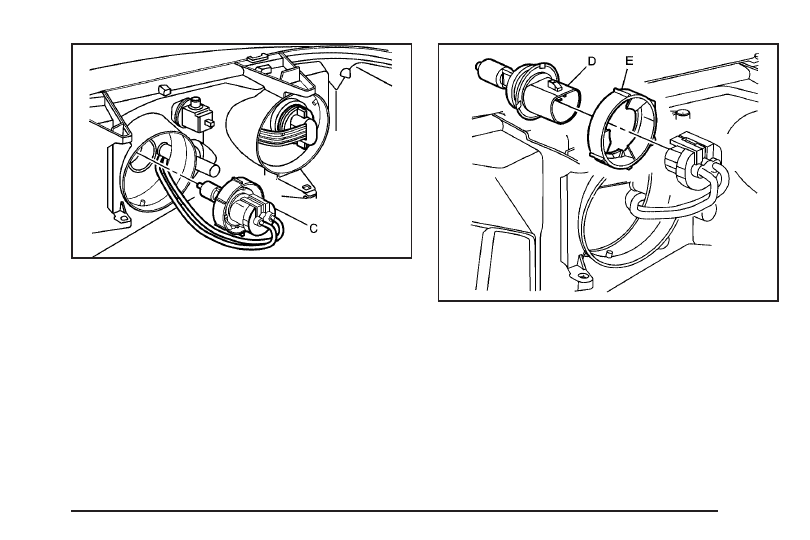
5. Raise the lock tab and pull the connector (C)
from the base of the bulb to remove the
electrical connector.
6. Remove the bulb retaining nut (E) by turning it
counterclockwise.
7. Remove the bulb (D) and replace it with the
appropriate bulb.
8. Reverse the steps to reinstall the lamp
assembly.
321