Snowmobile Polaris DEEP SNOW (2005 year). Manual - part 61
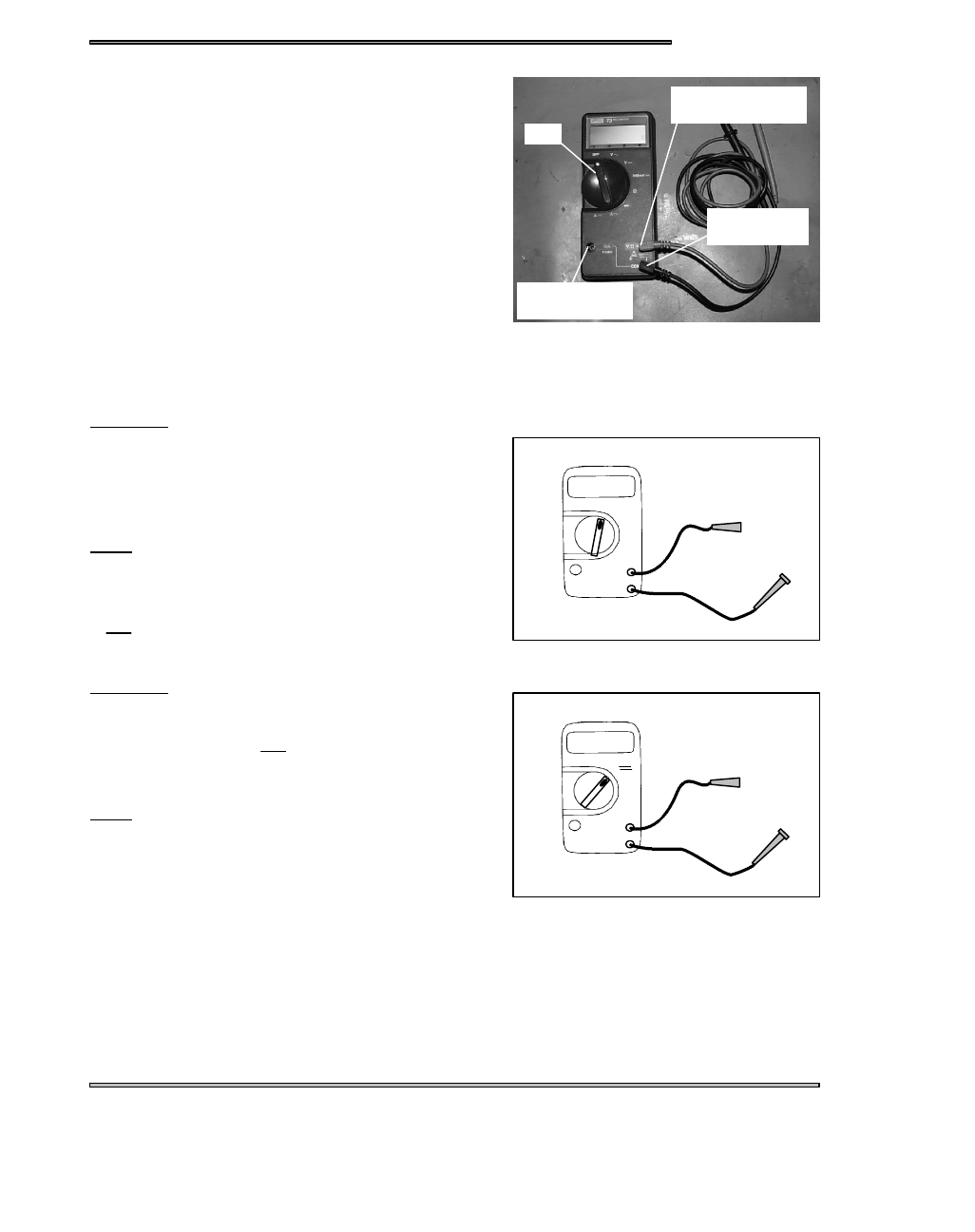
ELECTRICAL
13.1
Typical Multimeter Usage
Multimeter Usage
The easiest and most accurate method for testing modern electri-
cal components is with a digital multitester. Any good quality multi-
tester will work. However, due to ease of operation and durability,
Polaris recommends the Fluke Model 73 (PN 2870659), or Tektro-
nix DMM155. See photo at right. This instrument will provide a dig-
ital readout of the measured value of the test being performed.
Listed below are the dial symbols, their meaning and what the dial
setting can be used for.
Off = Instrument Off
V~ = Volts AC - measuring alternator output
Used to measure AC voltage in an electrical system. AC voltage
is produced from every coil on the stator plate when a magnet is
passed by it.
Test Method
1. Connect black lead to Com (--) meter terminal.
2. Connect red lead to V
Ω
(+) meter terminal.
3. Turn selector dial to V
~
setting.
4. Connect test leads parallel with test component. The polarity of
the leads is not important.
Usage
S
Test unregulated voltage output of a stator coil
S
Test regulated voltage to the lights and handwarmers
V - - - = Volts DC - measuring battery voltage, volt drop, etc.
Used to measure DC voltage produced by a battery or rectifier.
Test Method
1. Connect black lead to Com (--) meter terminal
2. Connect red lead to V
Ω
(+) meter terminal.
3. Turn selector dial to V - - - setting.
4. Connect test leads parallel with test component. Observe
polarity.
Usage
S
Test battery voltage
S
Test DC regulator
S
Test voltage drop for bad connections
S
Test supply voltage to electric fuel gauge
Dial
Red Lead here
for Volts and Ohms
Common
(Black Lead)
Red Lead here
for Amperes
+
_
17.29
V
~
VAC
+
_
12.95
V
VDC