Iveco Stralis AT/AD. Manual - part 323
74601
74602
1)
Turn the key to START.
2)
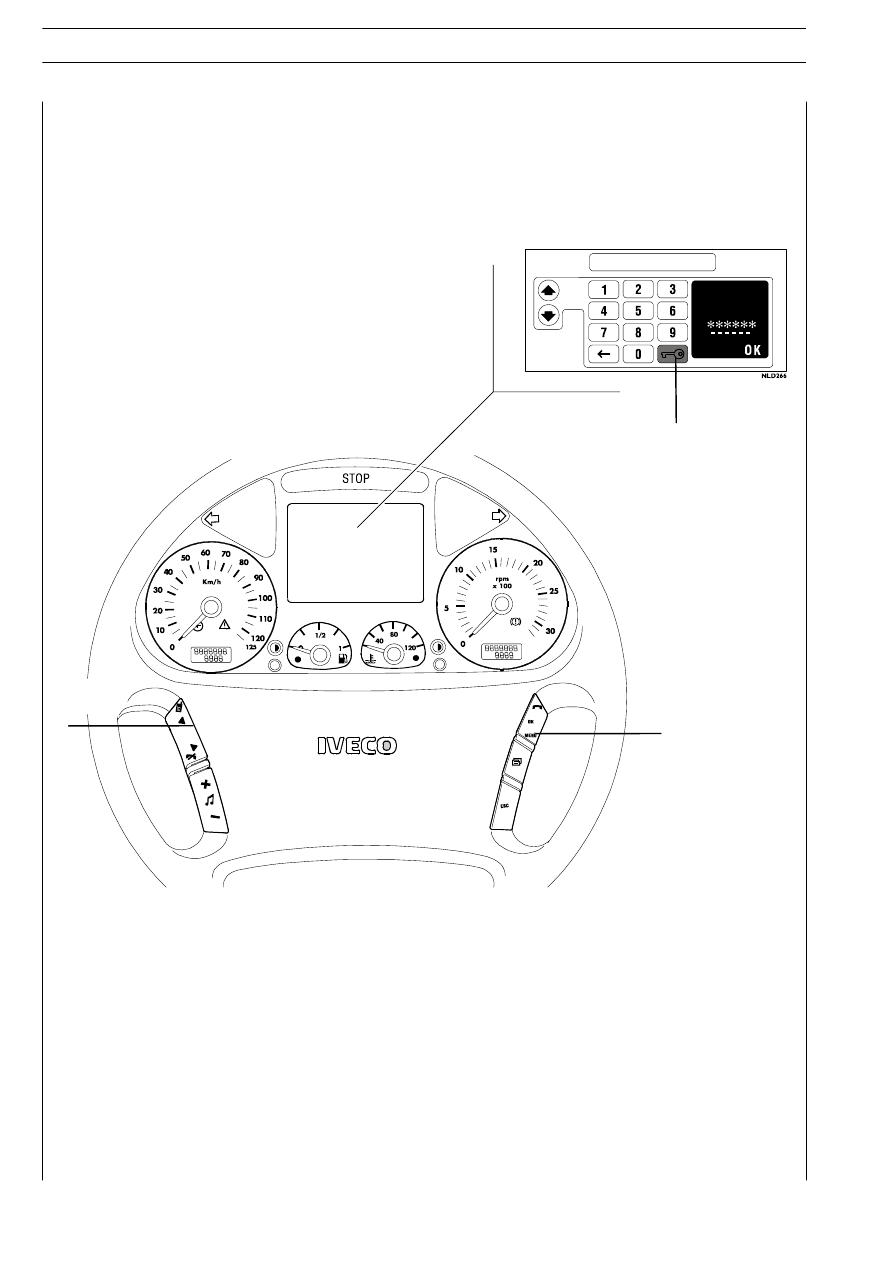
The display shown in the figure appears.
3)
Select the first digit of the ELECTRONIC CODE with push buttons ARROW UP and ARROW DOWN (A).
4)
Confirm the digit selected with OK (C).
5)
Continue with the remaining digits of the ELECTRONIC CODE.
6)
When the entire ELECTRONIC CODE is entered, select (B) and confirm with OK (C).
IMMOBILIZER
ENTER
CODE
press
B
C
A
III.76
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
S
TRALIS
AT/AD
Base - January 2003
It enables engine start when the key cannot be recognised or the IMMOBILIZER centre is down. Entering the electronic
code shown on the CODE CARD and operating the steering wheel push buttons can start the engine.