Chrysler Sebring, Stratus sedan, Sebring Convertible. Manual - part 649
methods may be used, but may not have all the ben-
efits of the recommended method.
NOTE: Only the 4 tire rotation method may be used
if the vehicle is equipped with a low mileage or tem-
porary spare tire.
DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Some vehicles are fitted with special high-perfor-
mance tires having a directional tread pattern. These
tires are designed to improve traction on wet pave-
ment. To obtain the full benefits of this design, the
tires must be installed so that they rotate in the cor-
rect direction. This is indicated by arrows on the tire
sidewalls.
When wheels and tires are being installed, extra
care is needed to ensure that this direction of rota-
tion is maintained.
Refer to Owner’s Manual for rotation schedule.
REMOVAL - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(1) Raise the vehicle so the tires clear ground
level. (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
HOISTING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) If the vehicle is equipped with wheel covers,
remove the cover from the wheel by prying it off with
an appropriate wheel cover removal tool.
(3) Remove the wheel mounting (lug) nuts from
the studs.
(4) Remove the tire and wheel assembly from the
hub.
INSTALLATION - TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
(1) To install the tire and wheel assembly, first
position it properly on the studs and hub mounting
surface using the hub pilot as a guide.
CAUTION: Never apply oil or grease to the wheel
mounting studs or nuts.
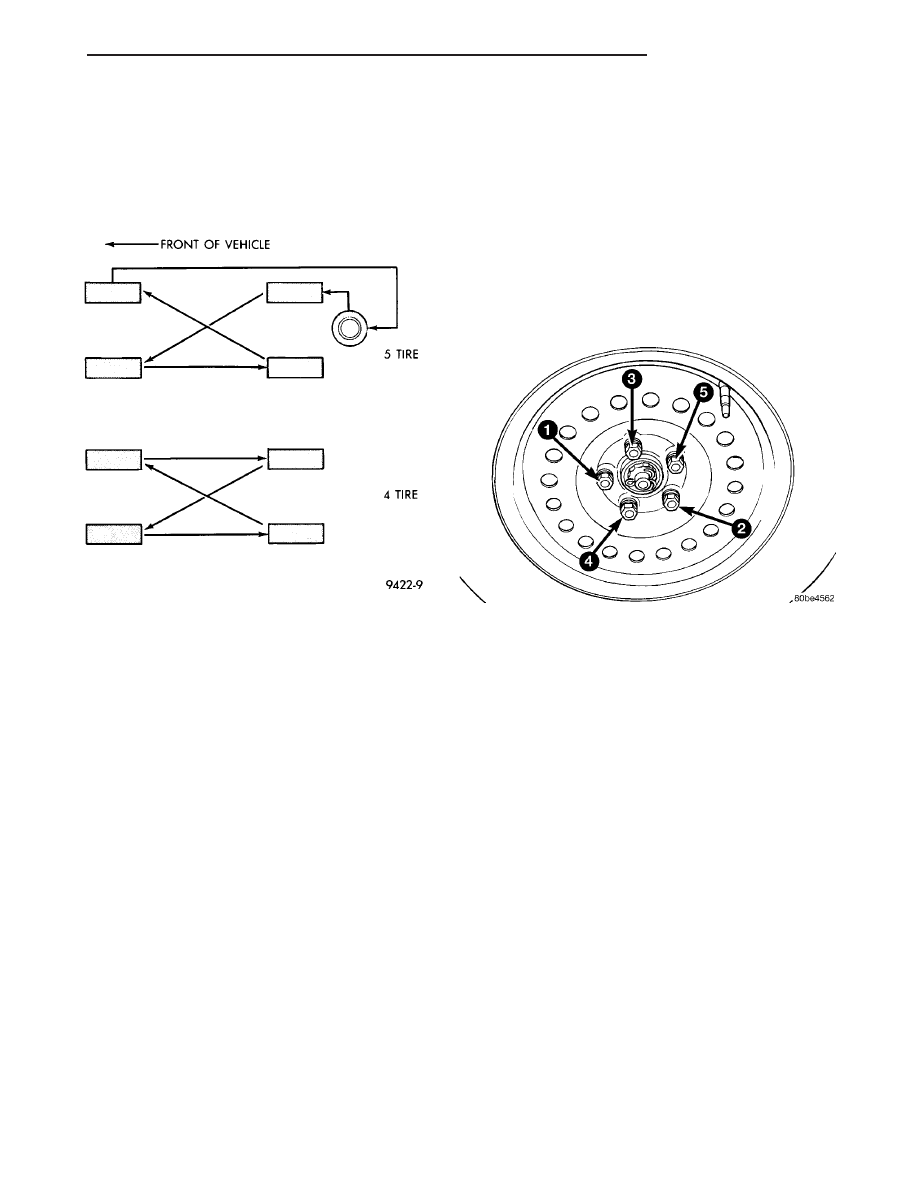
(2) Install and progressively tighten the five wheel
mounting (lug) nuts in the proper sequence (Fig. 12)
until half the specified torque is reached. Repeat the
sequence, tightening the wheel mounting (lug) nuts
to a final torque of 135 N·m (100 ft. lbs.).
(3) If equipped with wheel covers, align the valve
stem notch in the wheel cover with the valve stem on
the wheel. By hand, tap the wheel cover onto the
wheel until it is fully seated against the wheel.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRE
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle’s requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
• Rapid acceleration
• Severe application of brakes
• High-speed driving
Fig. 11 Forward-Cross Tire Rotation Method
Fig. 12 Wheel Nut Tightening Sequence
JR
TIRES/WHEELS
22 - 7
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)