Chrysler Le Baron, Dodge Dynasty, Plymouth Acclaim. Manual - part 572
Camshaft bearing journals and lobe wear. Lobe
wear should not exceed .25mm (.010 inch). To mea-
sure cam lobe wear (Fig. 8), measure lobe diameter
in two places at the largest diameter (over the nose).
Take first reading with micrometer in unworn area
at the edge of the lobe. Take second reading in the
worn area where rocker arm contacts the lobe. Sub-
tract second reading from the first. The difference is
the cam lobe wear.
CAMSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Oil camshaft journals and install camshaft
without cam followers. Tighten screws to specified
torque.
(2) Using a suitable tool, move camshaft as far
rearward as it will go.
(3) Zero dial indicator (Fig. 9).
(4) Move camshaft as far forward as it will go.
(5) End play travel: 0.13 - 0.33mm (0.005 - 0.013
inch.).
(6) Remove bearing caps and camshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install cam followers in correct order as re-
moved.
(2) Align camshaft bearing caps in proper sequence
with Cap No. 1 at timing belt end and Cap No. 5 at
transmission end. Arrows on Caps No. 1, 2, 3, 4
must point toward timing belt to prevent cap break-
age (Fig. 11).
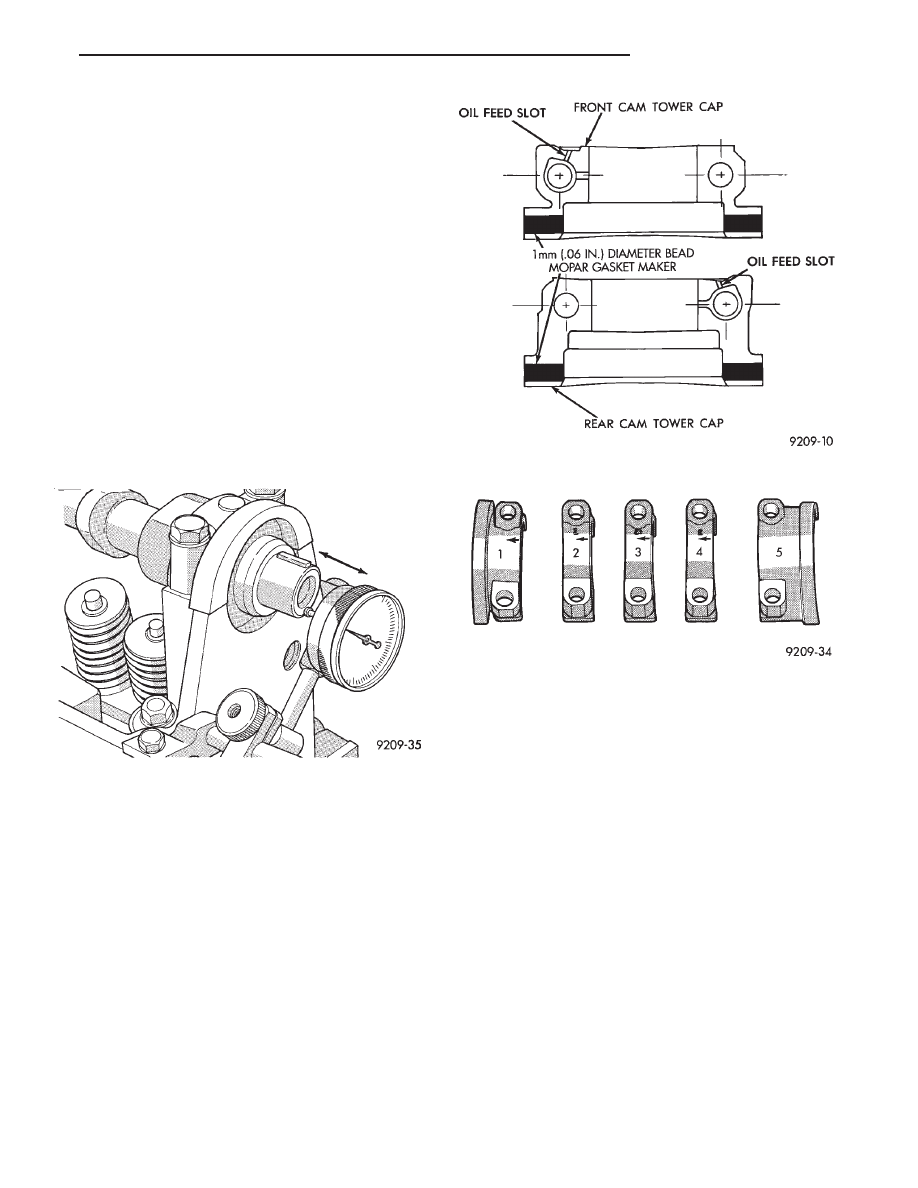
(3) Apply Mopar Gasket Maker to No.1 and No.5
bearing cap (Fig. 10).
(4) Caps must be installed before camshaft seals
are installed.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Refer to Lash Adjuster and Tappet Noise - Di-
agnosis in Standard Service Procedures, this Group.
VALVE COMPONENTS REPLACE—CYLINDER
HEAD NOT REMOVED
ROCKER ARM AND HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve cover.
(2) For each rocker arm, rotate cam until base cir-
cle is in contact with rocker arm. Depress valve
spring using Special Tool C-4682 (Fig. 12) and slide
rocker arm out. Keep rocker arms in order for reas-
sembly.
(3) Remove hydraulic lash adjuster.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install hydraulic lash adjusters making sure
that adjusters are at least partially full of oil. This is
indicated by little or no plunger travel when the lash
adjuster is depressed.
(2) Rotate cam until base circle is in contact posi-
tion with rocker arm. Depress valve spring with Spe-
cial Tool C-4682 (Fig. 12) and slide rocker arm in
place. Keep rockers in order. It is possible for the
Fig. 9 Camshaft End Play
Fig. 10 Cam Tower Cap Sealing
Fig. 11 Camshaft Bearing Caps Installation
Ä
2.2/2.5L ENGINE
9 - 25