Chrysler Le Baron, Dodge Dynasty, Plymouth Acclaim. Manual - part 287
nal. From the pick-up signal, the PCM determines
engine speed and ignition timing (coil dwell). If the
PCM does not receive a distributor signal when the
ignition switch is in the Run position, it will de-en-
ergize both relays. When the relays are de-energized,
battery voltage is not supplied to the fuel injector, ig-
nition coil, fuel pump and oxygen sensor heating el-
ement.
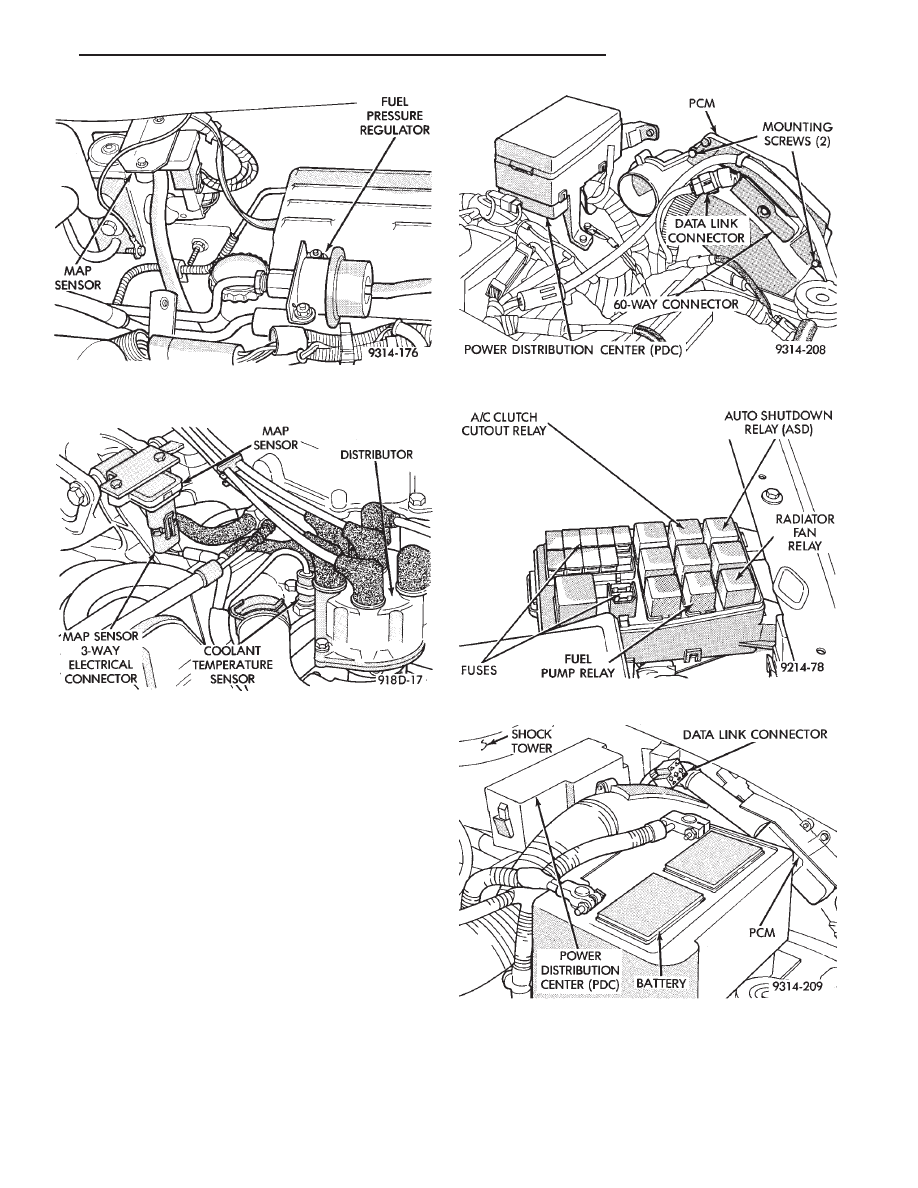
On AC, AG, AJ and AY models, the ASD relay and
fuel pump relay are located in the power distribution
center (Fig. 24, 25, 26, or 27).
On AA and AP models, the ASD relay and fuel
pump relay are mounted on the drivers side fender
well, next to the strut tower (Fig. 28).
IGNITION COIL
The 2.2L TBI, 2.5L TBI, 2.5L MPI and 3.0L en-
gines use an epoxy type coil. The coils are not oil
filled. The windings are embedded in a heat and vi-
bration resistant epoxy compound.
The powertrain control module (PCM) operates the
ignition coil through the auto shutdown (ASD) relay.
When the relay is energized by the PCM, battery
voltage is connected to the ignition coil positive ter-
minal. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive an input from the distributor pick-
Fig. 22 MAP Sensor—2.5L MPI (Flexible Fuel
AA-Body) Engines
Fig. 23 MAP Sensor—3.0L Engine
Fig. 24 Power Distribution Center (PDC) (AC Body)
Fig. 25 Relay Identification (AC Body)
Fig. 26 Power Distribution Center (PDC) (AG and AJ
Body)
Ä
IGNITION SYSTEMS
8D - 9