Chrysler Le Baron, Dodge Dynasty, Plymouth Acclaim. Manual - part 251
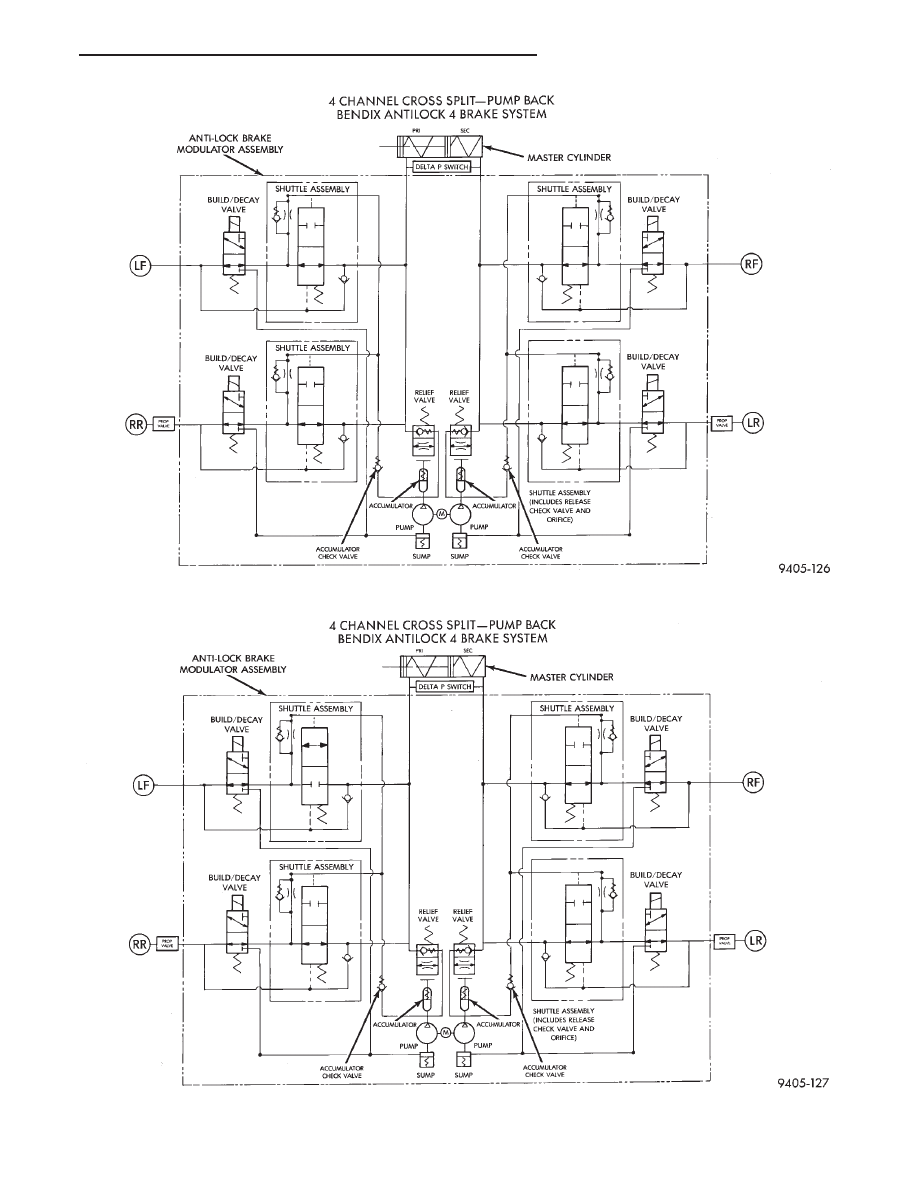
Fig. 1 Normal Braking - Hydraulic Control
Fig. 2 Build Pressure - Hydraulic Control (Left Front Wheel Shown)
Ä
ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM
5 - 21
|
|
|

Fig. 1 Normal Braking - Hydraulic Control Fig. 2 Build Pressure - Hydraulic Control (Left Front Wheel Shown) Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 21 |