Chrysler Le Baron, Dodge Dynasty, Plymouth Acclaim. Manual - part 250
fice (restriction) in the line between the wheel and
the Build/Decay Valve. This restriction provides a
controlled build rate to each wheel brake during an
Antilock stop. The Shuttle Orifice Valve will remain
in the orificed position until the ABS cycle is com-
plete. When the ABS cycle has been completed the
Build/Decay valves will return to their released posi-
tion which will equalize the pressure across the
Shuttle Orifice Valves. When the pressure equalizes,
the spring loaded Shuttle Orifice valves will return
to the unrestricted position.
FLUID SUMPS
There are two Fluid Sumps in the Hydraulic As-
sembly, one for the primary and secondary hydraulic
circuits. The Fluid Sumps store the brake fluid that
is decayed from the wheel brakes during an ABS cy-
cle. This fluid is then pumped to an accumulator
and/or the hydraulic system in order to provide build
pressure. The typical pressure in the sumps is 50 psi,
during ABS operation only.
HYDRAULIC SPRING ACCUMULATOR
The Hydraulic Spring Accumulators (Fig. 3) (one
on each circuit) are used to store pressurized hydrau-
lic brake fluid during ABS operation only. This fluid
is used during hard braking when the ABS system is
activated, to supplement brake pressure when re-
quired. During normal Non ABS brake operation
there is NO pressurized brake fluid stored in the ac-
cumulators. The Hydraulic Spring Accumulators are
not a serviceable part of the Modulator Assembly
and should never be removed from the assembly.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL SWITCH
The Pressure Differential Switch on the Bendix An-
tilock 4 Brake System is located on the frame rail
mounted brake hydraulic tube junction block. This
switch functions the same as the Pressure Differential
Switch located in the combination valve on standard
non ABS brake system. The pressure differential
switch monitors the primary and secondary hydraulic
brake circuits for a difference in pressure. A pressure
difference greater than 225 psi., will move and latch
the switch, grounding the Red Brake Warning Light
circuit. This will in turn, turn on the Red Brake
Warning Light in the instrument panel to warn the
driver of a pressure loss in one of the brake hydraulic
systems. This pressure differential switch is a replace-
able item of the junction block assembly. The Red
Brake Warning Light only indicates a problem
with the foundation brake hydraulic system and
not the Antilock system.
PUMP/MOTOR ASSEMBLY
The Modulator Assembly contains 2 Pump Assem-
blies, one each for the primary and secondary hydrau-
lic circuits. Both pumps are driven by a common
electric motor which is part of the Modulator Assembly.
The pumps take brake fluid from the sumps to supply
pressure to the accumulators or hydraulic system via
the shuttle orifice during an Antilock stop. The motor
only runs during an ABS stop and is controlled by the
CAB via the Pump/Motor Relay. The Pump/Motor
Assembly is not a serviceable item. If it requires
service the Modulator Assembly must be replaced.
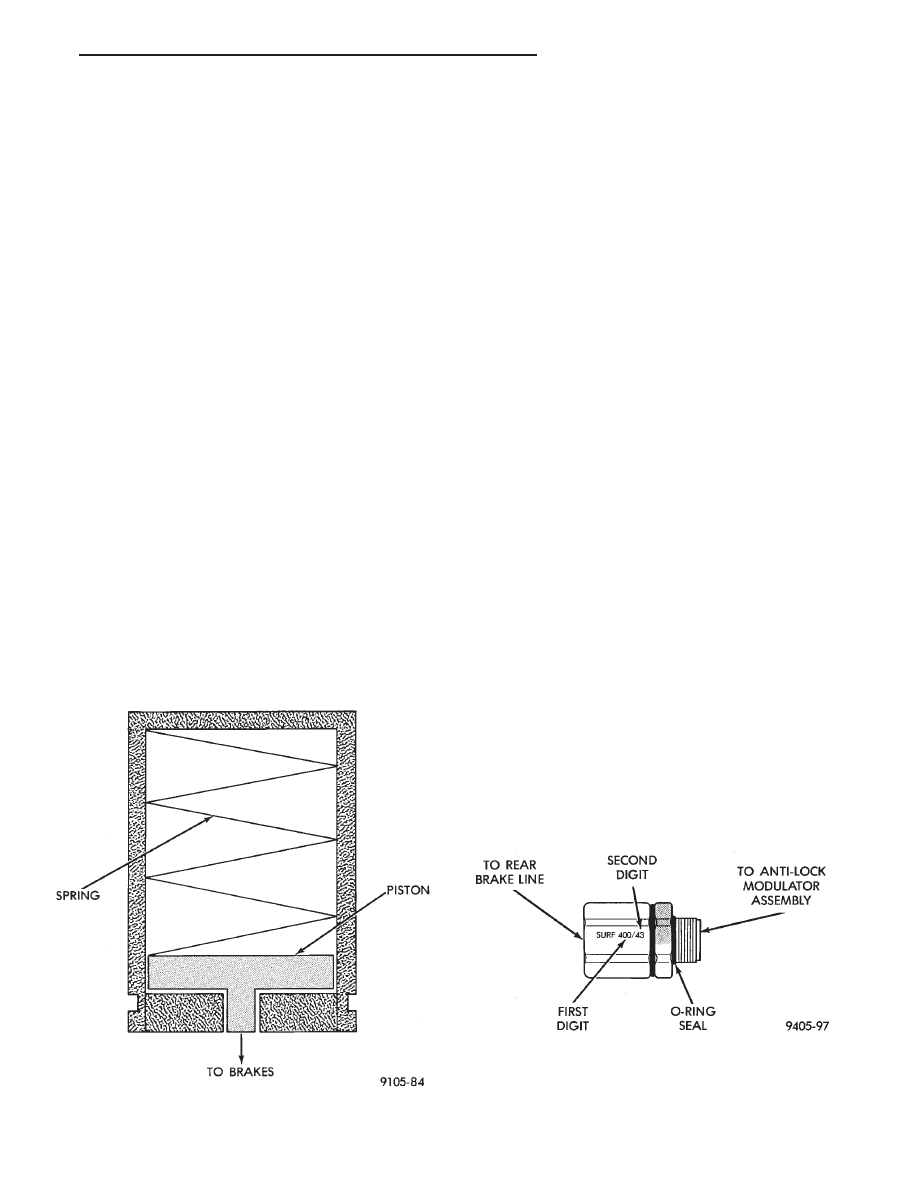
PROPORTIONING VALVES
Two Proportioning Valves (Fig. 4) are used in the
Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System, one for each of the
rear wheel brake hydraulic circuits. The Proportioning
Valves function the same as in a standard brake
system. The Proportioning Valves are located on the
side of the modulator assembly (Fig. 1). Each rear
wheel hydraulic brake line, is connected to an indi-
vidual proportioning valve.
Fig. 3 Hydraulic Spring Accumulator
Fig. 4 Proportioning Valve Identification
Ä
ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM
5 - 17