Chrysler Le Baron, Dodge Dynasty, Plymouth Acclaim. Manual - part 37
The exhaust gas oxygen content input is not ac-
cepted by the PCM during wide open throttle opera-
tion. The PCM will enrichen the air/fuel ratio to
increase performance and compensate for increased
combustion chamber temperature.
The PCM determines the methanol content of the
fuel from the methanol concentration sensor input.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. When the ignition
switch is turned to the OFF position, the following
occurs:
• All outputs are turned off.
• No inputs are monitored.
• The PCM shuts down.
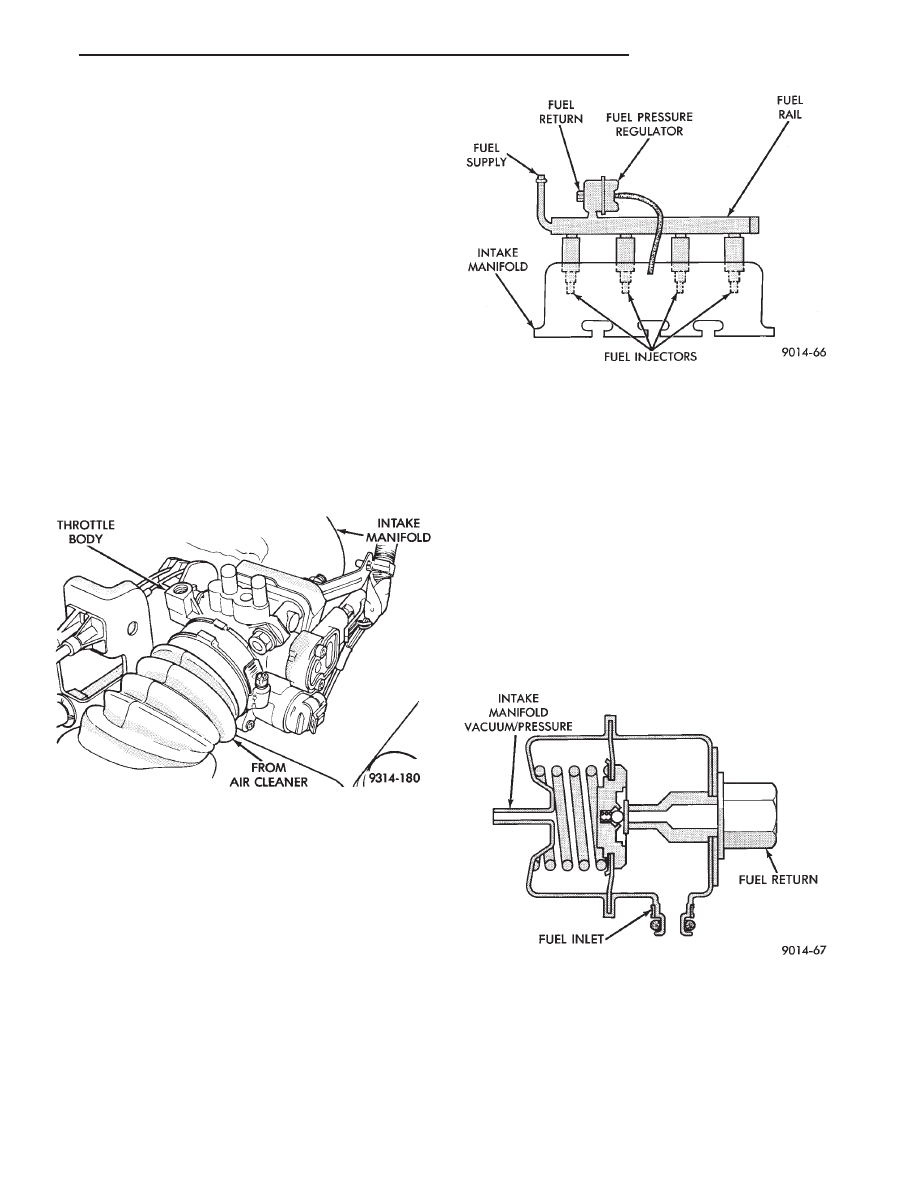
THROTTLE BODY
The throttle body houses the throttle position sen-
sor (TPS) and the idle air control motor (Fig. 15). Air
flow through the throttle body is controlled by a ca-
ble operated throttle blade at the base of the throttle
body.
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT
Fuel is pumped to the fuel rail by an electrical
pump in the fuel tank. A filter, attached to the pump
inlet, prevents water and other contaminants from
entering the fuel supply circuit.
The vacuum assisted fuel pressure regulator keeps
fuel pressure at 380 kPa (55 psi). The regulator uses
intake manifold pressure at the vacuum tee as a ref-
erence.
FUEL INJECTORS AND FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
Four fuel injectors are retained in the fuel rail by
lock rings (Fig. 16). The fuel injectors and rail bolt in
position with the injectors inserted into recessed
holes in the intake manifold.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
The pressure regulator is located downstream of
the fuel injector on the fuel rail (Fig. 17). The regu-
lator maintains constant 380 kPa (55 PSI) fuel pres-
sure across the fuel injector tip.
The regulator has a spring loaded rubber dia-
phragm that uncovers a fuel return port. When the
fuel pump operates, fuel flows past the injector into
the regulator. Fuel is restricted from flowing any fur-
ther by the blocked return port. When fuel pressure
reaches 380 kPa (55 PSI), it pushes on the dia-
phragm, compresses the spring, and uncovers the
fuel return port. The diaphragm and spring continu-
ally move from an open to closed position keeping
the fuel pressure consistent.
Fig. 15 Throttle Body
Fig. 16 Fuel Supply System
Fig. 17 Fuel Pressure Regulator
Ä
FUEL SYSTEMS
14 - 65