Chrysler PT Cruiser. Manual - part 724
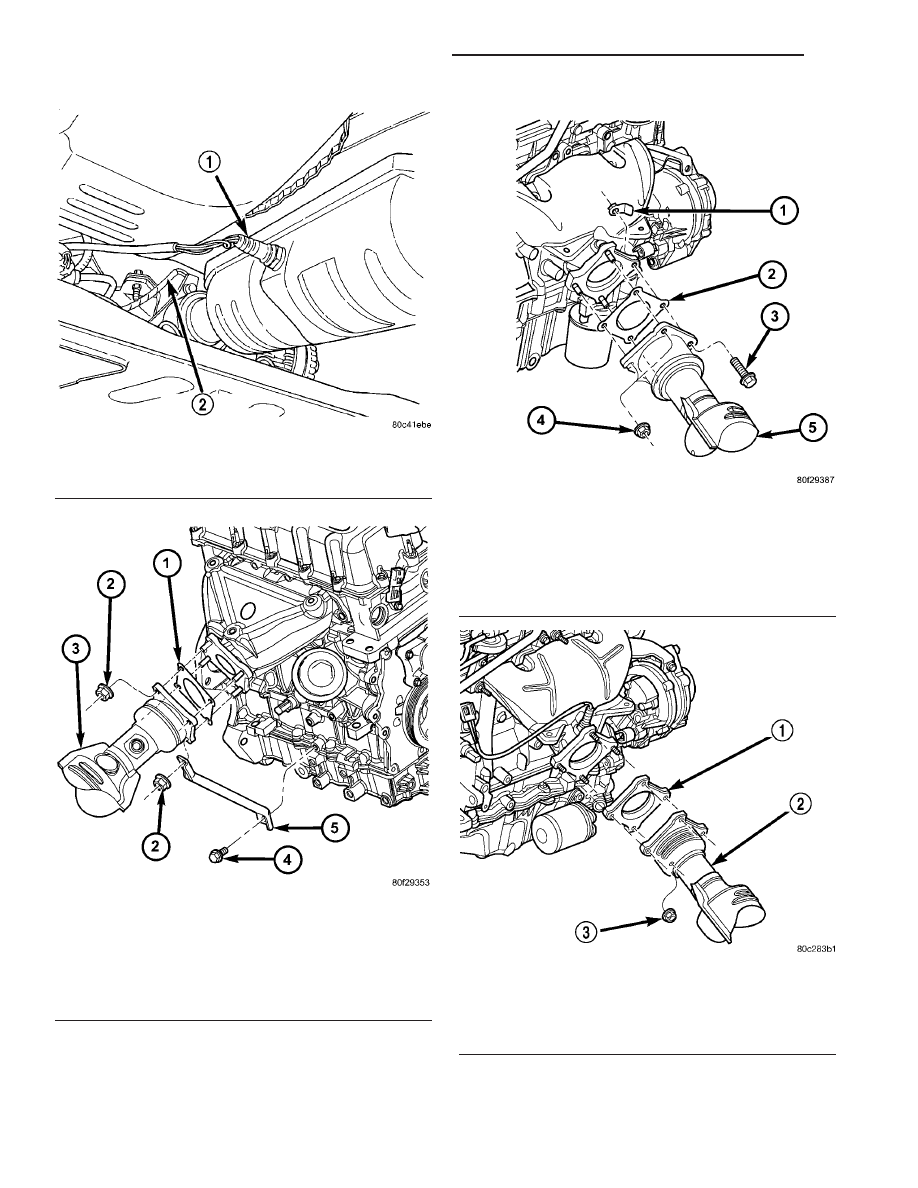
Fig. 8 Downstream 1/2 Oxygen Sensor - Typical
1 - DOWN STREAM O2 SENSOR
2 - UP STREAM O2 SENSOR
Fig. 9 Converter to Exhaust Manifold Connection -
1.6L
1 - GASKET
2 - NUT
3 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
4 - BOLT
5 - SUPPORT BRACKET
Fig. 10 Converter to Exhaust Manifold Connection -
2.0L
1 - FLAG NUT
2 - GASKET
3 - BOLT
4 - NUT
5 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
Fig. 11 Converter to Exhaust Manifold Connection -
2.4L
1 - GASKET
2 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
3 - NUT
11 - 10
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND TURBOCHARGER
PT
CATALYTIC CONVERTER (Continued)