Dodge Dakota (ND). Manual - part 63
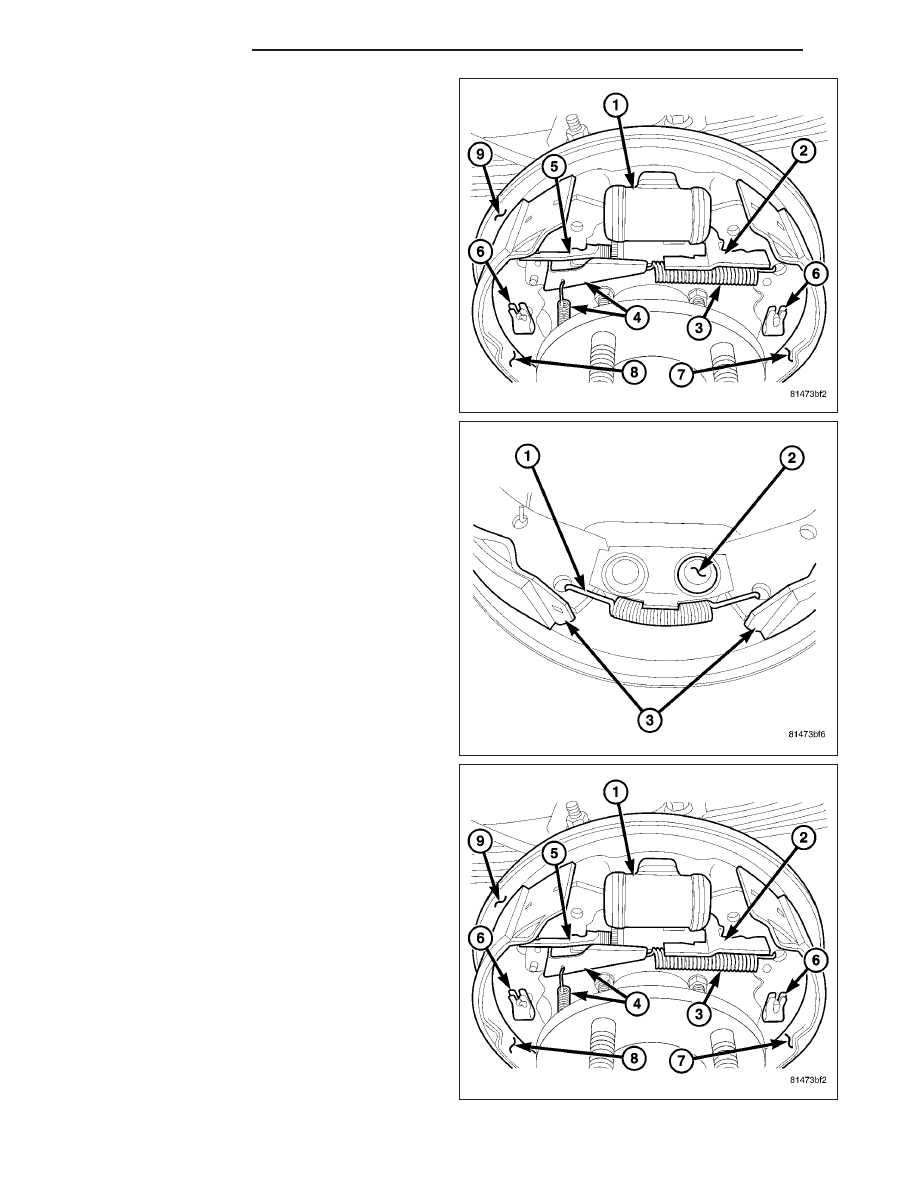
4. Install parking brake lever (2) to the rear shoe (7)
and install the hold down clip (6).
5. Install the adjuster strut (5) onto the shoes and
park brake lever (2).
6. Install the front shoe (8) on support plate (9). and
install the hold down clip (6).
7. Install the adjuster spring and lever (4) in the slot in
the adjuster strut (7).
8. Install the lower return spring (1) to the shoes (3).
9. Verify adjuster operation. Pull both shoes outward
to move the adjuster lever (4) to rotate the star
wheel. Be sure adjuster lever properly engages
star wheel teeth.
10. Adjust brake shoes to drum with brake gauge.
11. Install wheel and tire assembly. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS
-
STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5 - 22
BRAKES - BASE
ND