SsangYong Stavic / SsangYong Rodius (2005 year). Manual - part 90
DI02-35
CHANGED BY
EFFECTIVE DATE
AFFECTED VIN
ENGINE HOUSING
DI ENG SM - 2004.9
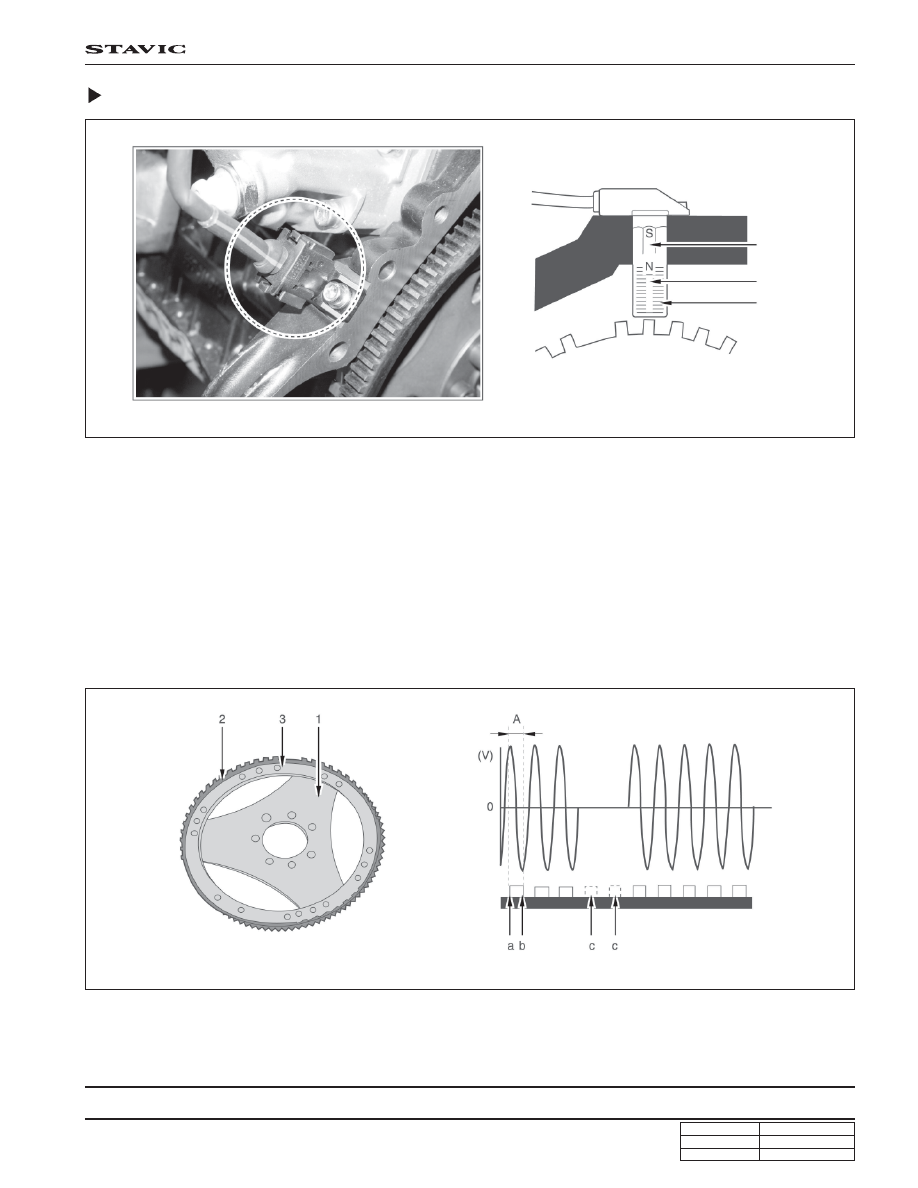
Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor is located near to flywheel on the rear of cylinder block. It generates AC voltage between
increment type driven plate that fixed on flywheel inside. The sensor consists of soft iron core that winded copper wire
on permanent magnet and generates sign wave AC voltage when magnetism on the sensor wheel passes the sensor.
When the crankshaft rotates, ‘+’ signal will be generated from near the front edge and ‘-’ signal will be generated from
near the rear edge among teeth on the driven plate near to crankshaft position. The AC voltage increases as the engine
speed increases, however, no signal occurs from the 2-missing-tooth on the increment type driven plate. By using these
teeth, ECU recognizes TDC of No. 1 and 5 cylinders.
ECU converts the alternative signals into digital signals to recognize crankshaft position, piston position and engine
speed. The piston position that coupled with crankshaft is main factor in calculating injection timing. By analyzing the
reference position and camshaft position sensor, can recognize No. 1 cylinder and calculate the crankshaft speed.
A. Distance between ‘+’ max. voltage and ‘-’ max.
voltage
a. Front edge
b. Rear edge
c . 2-missing-tooth
<Location of crankshaft position sensor>
<Drive plate>
<Structure of crankshaft position sensor>
Permanent
magnet
Ring gear
Iron
coil
Standard
position