SsangYong Musso. Manual - part 471
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-61
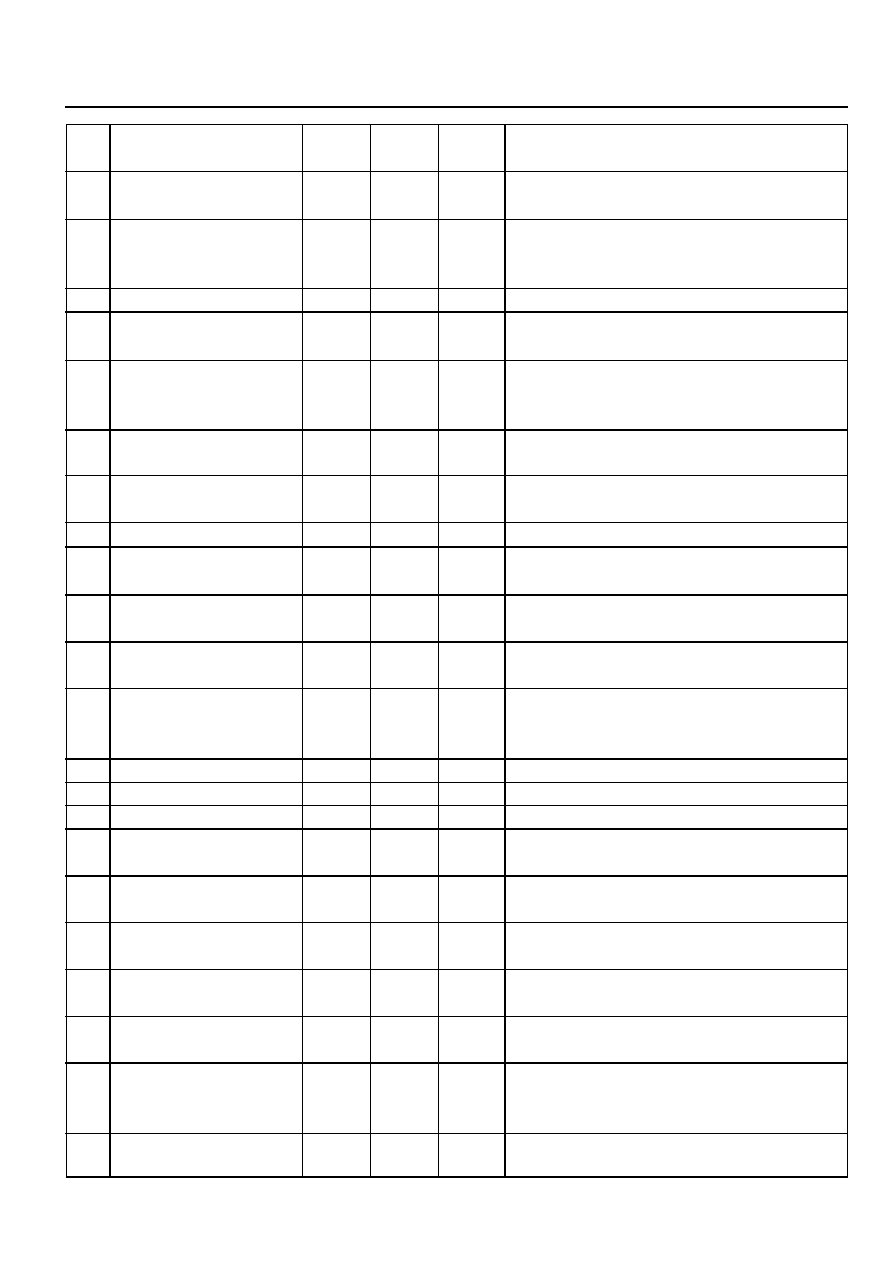
Pin
No.
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
Identification
Mode Indicator Lamp -
‘Power’
Throttle Position Sensor
Output as Pulse Width
Modulation for TOD
Air Conditioner Input Signal
Kickdown Switch
Mode Switch
Transfer Case Input
(High) -4WD Lamp High
Ignition Switch
Do not use
Gear Position ‘1’ Lamp/
Gear Position Code 1
*Gear Position ‘2’ Lamp/
Gear Position Code 2*
Gear Position ‘3’ Lamp/
Gear Position Code 3*
Gear Position ‘Drive’
Lamp/
Gear Position Code 4*
CAN (-ve)
CAN (+ve)
K-line Communication Link
Engine Speed Input
Sensor (+ve)
Road Speed Pulses
Shaft Speed Sensor
Signal
Throttle Position Sensor -
Ground
Throttle Position Sensor -
Reference
Throttle Position Sensor -
Input Signal
Transfer(or Case Input
(Low) - 4WD Lamp Low
Type
OP
OP
-
IP
IP
IP
IP
-
OP
OP
OP
OP
I/O
I/O
I/O
IP
OP
IP
GND
REF
IP
IP
Description
Indicates ‘POWER’ mode shift schedule is se-
lected.
Provides an analogue signal of the throttle po-
sition for the Torque on Demand (TOD) Con-
trol Module.
Input
Switch to indicate when a kickdown is required
at high throttle position.
Switch to select ‘NORMAL’, ‘POWER’ or ‘WIN-
TER’ shift schedule.
Voltage varies from OV to 12V.
Switch to indicate 4WD’HIGH RANGE’ is se-
lected.
Ignition power is used as the main power source
to drive the unit and the solenoids.
Drives jewel in the instrument cluster to indi-
cate
gear leverposition’1'. Drives jewel in the instru-
ment cluster to indicate
gear lever position’2'. Drives jewel in the instru-
ment cluster to indicate gear lever position’3'.
Drives jewel in the instrument cluster to indi-
cate
‘DRIVE’. gear lever position.
CAN low side bus communication (CANL).
CAN high side bus communication (CANH).
Diagnostic information and vehicle coding.
Flywheel/Ring gear pulses to indicate engine
speed.
Road speed signals derived from shaft speed
sensors.
This sensor transmit shaft speed signal to the
TCU.
Throttle position sensor ground.
This is the 5V reference voltage supply gener-
ated by the unit for the throttle position sensor.
This sensor is a resistance potentiometer indi-
cating throttle position.
Voltage varies 0V to 5V.
Switch to indicate 4WD’LOW RANGE’ is se-
lected.
4WD
(Diesel)
O
O
O
O
!
!
!
4WD
(Gas)
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!