Frelander 2. Manual - part 284
module)
, regulates the amount of exhaust gases recirculated into the air intake system. The
ECM
uses signals from
various engine sensors and calculates a response based on the embedded software algorithm to control exhaust gas
recirculation. The
ECM
transmits this control signal to the valve's actuator, which is closed-loop controlled with the mass
air flow (MAF) sensor providing the feedback to the
ECM
.
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
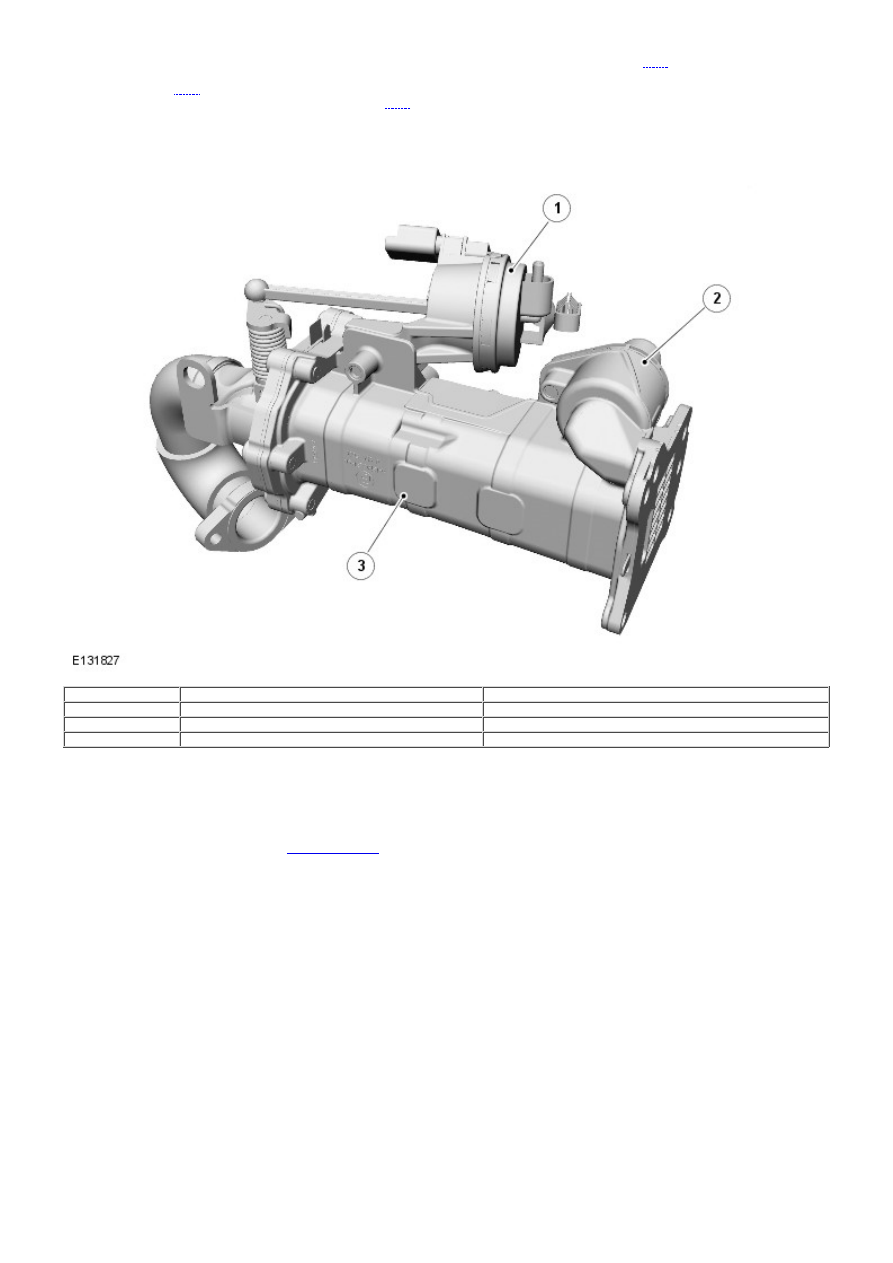
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve and Cooler Assembly
Item
Part Number
Description
1
-
Actuator
2
-
Coolant outlet
3
-
Cooler
The EGR valve and cooler assembly is located on the RH side of the cylinder head above the exhaust manifold, and
secured with 4 fixings. An inlet pipe connects the EGR cooler to the exhaust manifold. A gas transfer tube is routed across
the engine and connects the EGR valve outlet to the intake manifold housing.
A pipe on the EGR cooler body connects to the climate control heater outlet hose, and provides the coolant supply to the
EGR cooler. The EGR cooler outlet connects to the coolant rail, located on the RH side of the engine. The coolant rail is
connected between the thermal control module and the coolant pump rear housing.
For additional information, refer to:
Engine Cooling
(303-03A Engine Cooling - I6 3.2L Petrol, Description and Operation).
The EGR is controlled by the ECM, and is enabled when the engine meets the correct operating temperatures and under
cruising conditions.
Oil Separator