Frelander 2. Manual - part 106
3
-
Dust shield
4
-
Dust shield retaining screw (3 off)
5
-
Brake disc
6
-
Brake disc retaining screw
7
-
Outer anti-squeal shim
8
-
Outer brake pad
9
-
Inner brake pad
10
-
Inner anti-squeal shim
11
-
Caliper housing spring
12
-
Fixed carrier
13
-
Caliper piston seal
14
-
Caliper piston
15
-
Sliding caliper
16
-
Bushed bolt rubber boot (2 off)
17
-
Bushed bolt (2 off)
18
-
Bushed bolt dust cap (2 off)
19
-
Caliper bleed screw
20
-
Bleed screw cap
21
-
Flexible hose
22
-
Fixed carrier retaining bolt (2 off)
23
-
Front Left-Hand (LH) wheel knuckle
OVERVIEW
The front brake assembly features a ventilated brake disc and cast-iron sliding caliper with single acting piston.
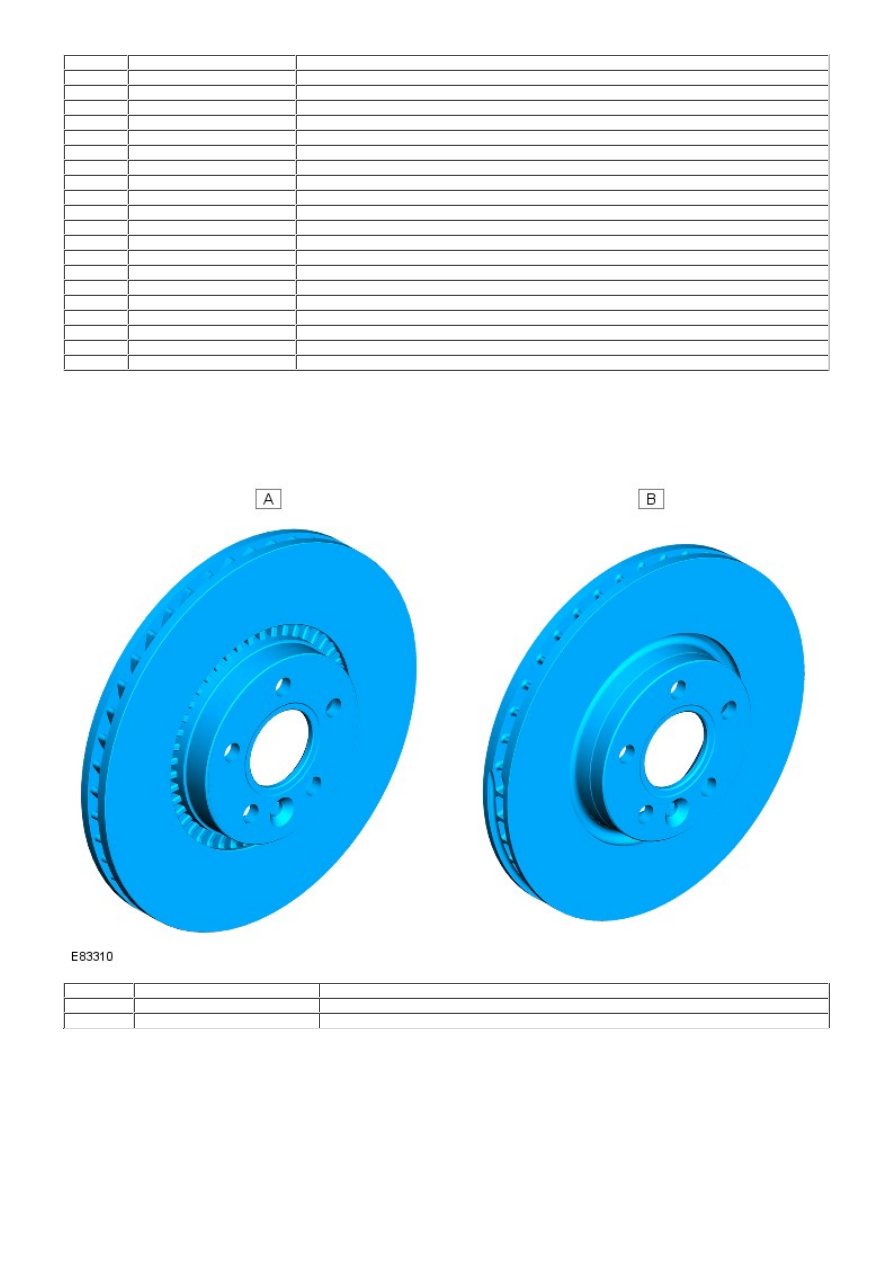
BRAKE DISC
Item
Part Number
Description
A
-
Front brake disc - i6 gasoline vehicle
B
-
Front brake disc - TD4 diesel vehicle
The brake disc installed to the 3.2 liter i6 gasoline vehicle is 316 x 28 mm (12.44 x 1.10 in) diameter. The brake disc
installed to the 2.2 liter TD4 diesel vehicle is 300 x 28 mm (11.81 x 1.10 in) diameter. The brake disc is secured to the
wheel knuckle hub with a single screw and is also retained by the 5 wheel securing nuts.
Both types of front brake disc are manufactured with ventilation channels, allowing the disc to achieve high levels of
thermal stability even during severe braking.
The disc is cooled as the forward motion of the vehicle draws air through the ventilation channels, and across the surfaces
of the disc.
CALIPER ASSEMBLY