Isuzu Rodeo UE. Manual - part 327
6E2–63
RODEO 6VD1 3.2L ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Electronic Ignition System Diagnosis
If the engine cranks but will not run or immediately stalls,
the Engine Cranks But Will Not Start chart must be used
to determine if the failure is the ignition system or the fuel
system. If DTC P0300 through P306, P0341, or P0336 is
set, the appropriate diagnostic trouble code chart must be
used for diagnosis.
If a misfire is being experienced with no DTC set, refer to
the
Symptoms section for diagnosis.
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
A continuous purge condition with no purge commanded
by the PCM will set a DTC P1441. Refer to the DTC
charts for further information.
Visual Check of The Evaporative
Emission Canister
f
If the canister is cracked or damaged, replace the
canister.
f
If fuel is leaking from the canister, replace the canister
and check hoses and hose routing.
Fuel Metering System Check
Some failures of the fuel metering system will result in an
“Engine Cranks But Will Not Run” symptom. If this
condition exists, refer to the
Engine Cranks But Will Not
Run chart. This chart will determine if the problem is
caused by the ignition system, the PCM, or the fuel pump
electrical circuit.
Refer to
Fuel System Electrical Test for the fuel system
wiring schematic.
If there is a fuel delivery problem, refer to
Fuel System
Diagnosis, which diagnoses the fuel injectors, the fuel
pressure regulator, and the fuel pump. If a malfunction
occurs in the fuel metering system, it usually results in
either a rich HO2S signal or a lean HO2S signal. This
condition is indicated by the HO2S voltage, which causes
the PCM to change the fuel calculation (fuel injector pulse
width) based on the HO2S reading. Changes made to the
fuel calculation will be indicated by a change in the long
term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a Tech
2. Ideal long term fuel trim values are around 0%; for a
lean HO2S signal, the PCM will add fuel, resulting in a fuel
trim value above 0%. Some variations in fuel trim values
are normal because all engines are not exactly the same.
If the evaporative emission canister purge is “ON,” the
long term fuel trim may be as low as –38%. If the fuel trim
values are greater than +23%, refer to
DTC P0131, DTC
P0151, DTC P0171, and DTC 1171 for items which can
cause a lean HO2S signal.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The Tech 2 displays the IAC pintle position in counts. A
count of “0” indicates the PCM is commanding the IAC
pintle to be driven all the way into a fully-seated position.
This is usually caused by a large vacuum leak.
The higher the number of counts, the more air is being
commanded to bypass the throttle blade. Refer to IAC
System Check in order to diagnose the IAC system.
Refer to
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling in
Symptoms for other possible causes of idle problems.
Fuel System Pressure Test
A fuel system pressure test is part of several of the
diagnostic charts and symptom checks. To perform this
test, refer to
Fuel Systems Diagnosis.
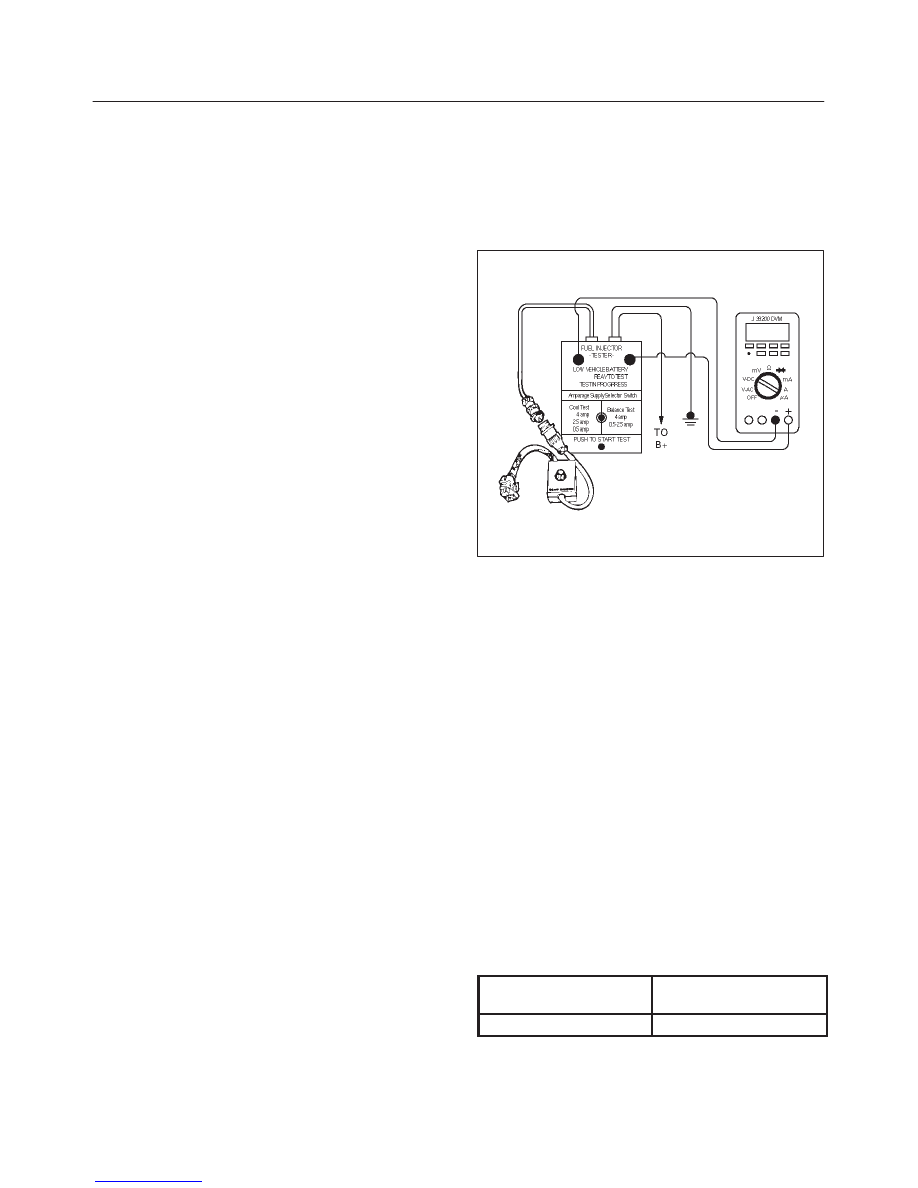
Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure and
Fuel Injector Balance Test Procedure
T32003
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Relieve the fuel pressure by connecting the J
34730–1 Fuel Pressure Gauge to the fuel pressure
connection on the fuel rail.
CAUTION: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the fuel
pressure connection. The towel will absorb any fuel
leakage that occurs during the connection of the fuel
pressure gauge. Place the towel in an approved
container when the connection of the fuel pressure
gauge is complete.
Place the fuel pressure gauge bleed hose in an
approved gasoline container.
With the ignition switch “OFF,” open the valve on the
fuel pressure gauge.
3. Record the lowest voltage displayed by the DVM
after the first second of the test. (During the first
second, voltage displayed by the DVM may be
inaccurate due to the initial current surge.)
Injector Specifications:
Resistance Ohms
Voltage Specification at
10
°
C-35
°
C (50
°
F-95
°
F)
11.8 – 12.6
5.7 – 6.6
f
The voltage displayed by the DVM should be within
the specified range.