Chrysler Sebring, Stratus sedan, Sebring Convertible. Manual - part 320
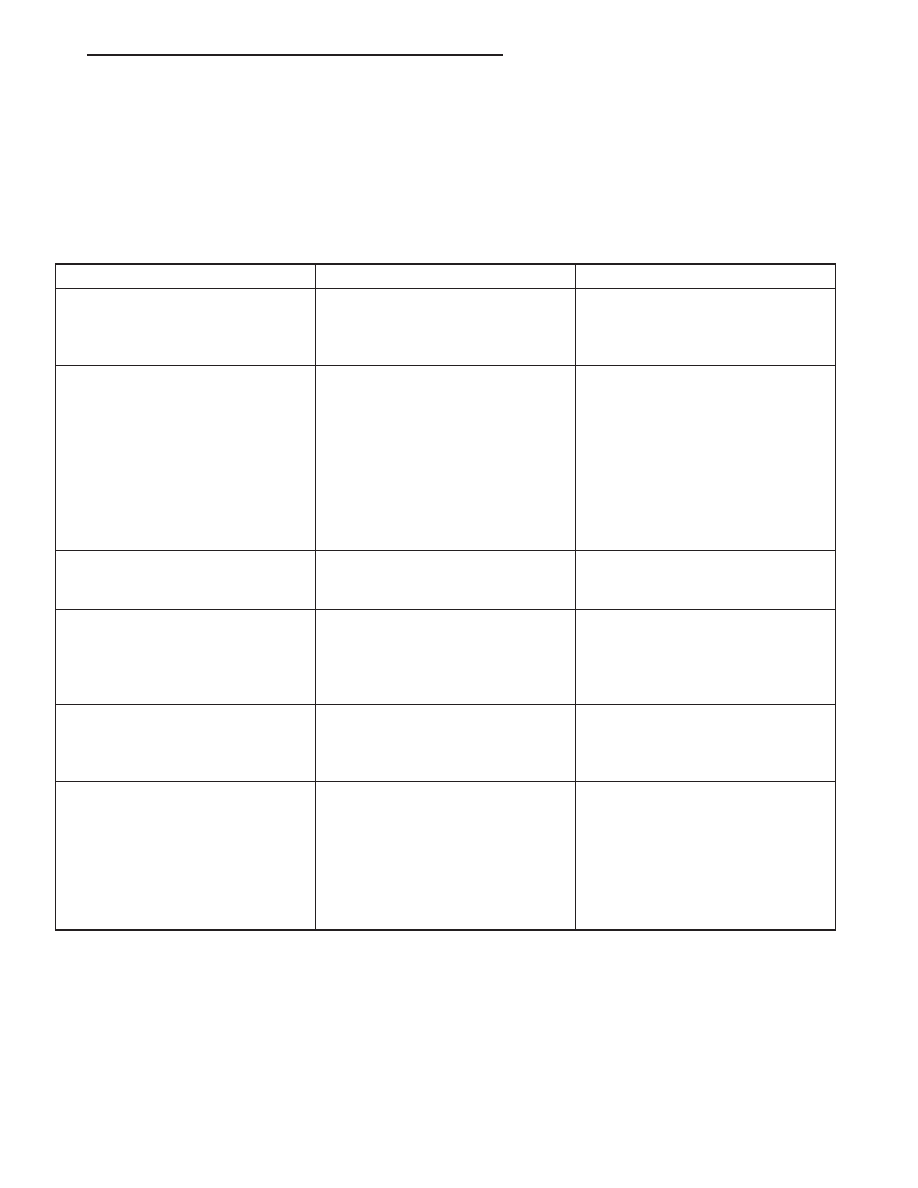
SHIFT SCHEDULES
The PCM has programming that allows it to select
a variety of shift schedules. Shift schedule selection
is dependent on the following:
• Shift lever position
• Throttle position
• Engine load
• Fluid temperature
• Software level
As driving conditions change, the PCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule
Condition
Expected Operation
Extreme Cold
Oil temperature at start-up below
-16° F
Park, Reverse, Neutral and 2nd
gear only (prevents shifting which
may fail a clutch with frequent
shifts)
Cold
Oil temperature at start-up above
-12° F and below 36° F
– Delayed 2-3 upshift
(approximately 22-31 mph)
– Delayed 3-4 upshift (45-53 mph)
– Early 4-3 costdown shift
(approximately 30 mph)
– Early 3-2 coastdown shift
(approximately 17 mph)
– High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
– No EMCC
Warm
Oil temperature at start-up above
36° F and below 80 degree F
– Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
– No EMCC
Hot
Oil temperature at start-up above
80° F
– Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
– Full EMCC, no PEMCC except to
engage FEMCC (except at closed
throttle at speeds above 70-83 mph)
Overheat
Oil temperature above 240° F or
engine coolant temperature above
244° F
– Delayed 2-3 upshift (25-32 mph)
– Delayed 3-4 upshift (41-48 mph)
– 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
– 3rd gear PEMCC from 27-31 mph
Super Overheat
Oil temperature above 260° F
– All
9
Overheat
9
shift schedule
features apply
– 2nd gear PEMCC above 22 mph
– Above 22 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
JR
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES
8E - 9
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)