содержание .. 590 591 592 593 ..
Toyota Sequoia (2005). Manual - part 592
I28198
I28199
I28200
I28201
I28202
–
DIAGNOSTICS
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
DI–2163
2357
(4)
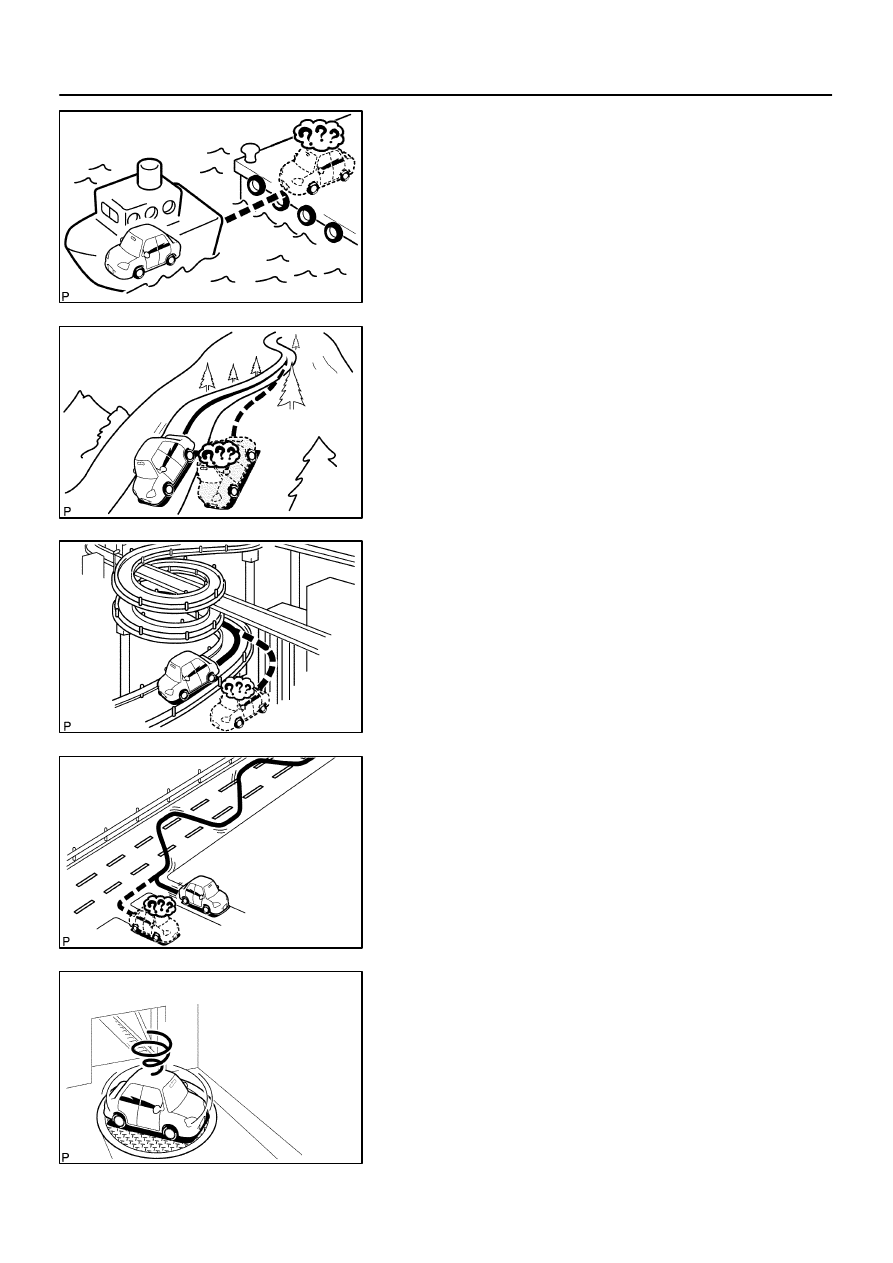
When the vehicle is carried, such as on a ferry, and
the vehicle itself is not running, the current vehicle
position mark may be displayed in the position
where the vehicle was until a measurement can be
performed by GPS.
(5)
When the vehicle runs on a steep hill, the current ve-
hicle position mark may deviate from the correct
position.
(6)
When the vehicle makes a continuous turn of 360,
720, 1,080, etc. degrees, the current vehicle posi-
tion mark may deviate from the correct position.
(7)
When the vehicle moves erratically, such as
constant lane changes, the current vehicle position
mark may deviate from the correct position.
(8)
When the ignition switch is turned to the ACC or ON
position on a turntable before parking, the current
vehicle position mark may not point in the correct
direction. The same will occur when the vehicle
comes out of parking.