SsangYong Korando II (1996-2006 year). Manual - part 250
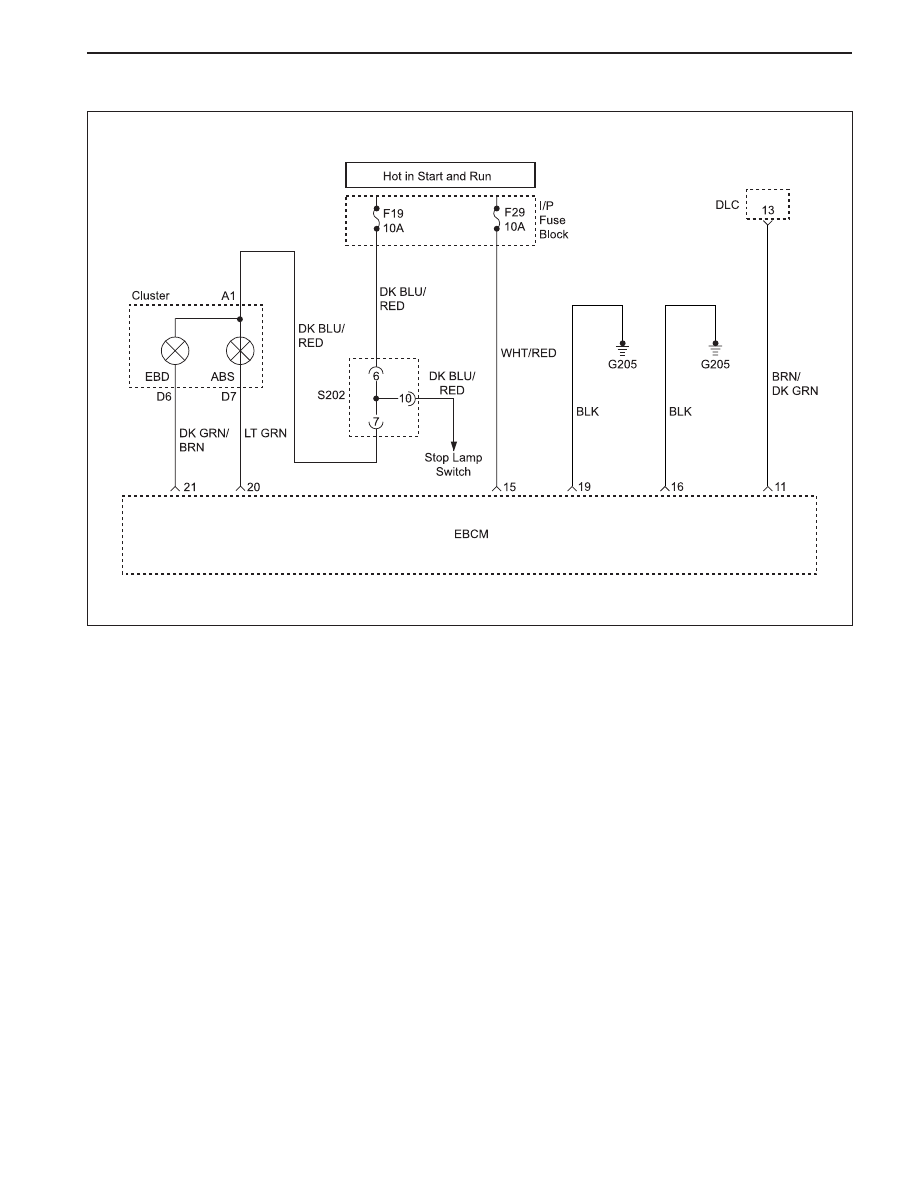
ABS AND TCS 4F-15
SSANGYONG MY2002
DIAGNOSIS
KAA4F110
DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK
The Diagnostic Circuit Check is an organized approach
to identifying a problem created by an antilock brake
system (ABS) malfunction. If must be the starting point
for any ABS complaint diagnosis because it directs
the service technician to the next logical step in
diagnosing the complaint.
Diagnostic Process
Perform the following steps in order when servicing
the ABS/TCS system. Failure to do so may result in
the loss of important diagnostic data and may lead to
difficulties and time-consuming diagnosis procedures.
1. Perform the tests of the table below.
2. Perform a road test if directed by the table.
•
Test drive the vehicle while using the snapshot
feature of the scan tool.
•
Perform normal acceleration, stopping, and
turning maneuvers.
•
If this does not reproduce the malfunction,
perform an ABS stop or TCS maneuver on a low
friction surface such as gravel.
3. Clear the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) after
all system malfunctions have been corrected.