Mitsubishi Eclipse. Technical Information Manual (1994) - part 61
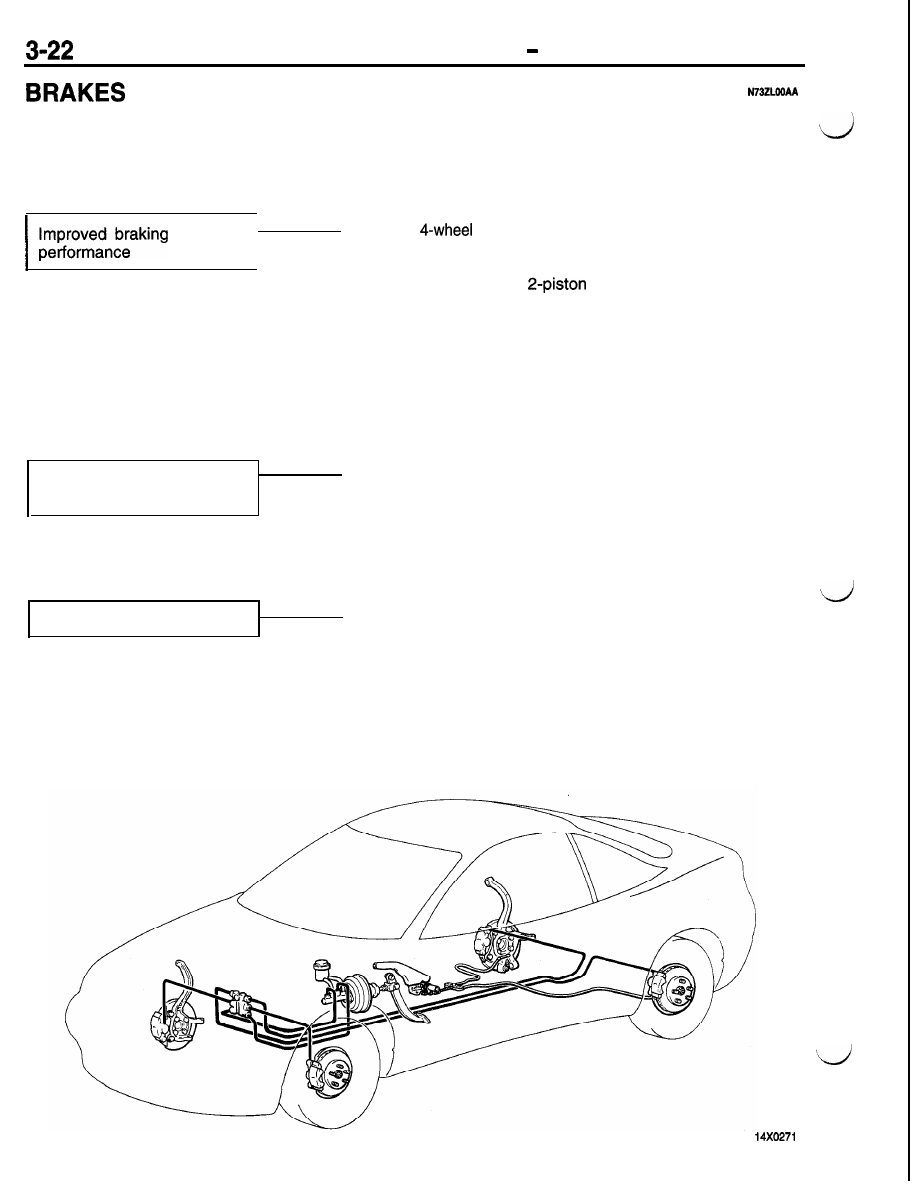
DRIVE-CONTROL COMPONENTS Brakes
The brake system offers high dependability and
and brake sensitivity.
durability along with improved braking performance
FEATURES
1.
The
anti-lock brake system (4ABS) prevents skid-
ding that may result from locked wheels, thereby assuring
safe braking.
2. For some models,
type ventilated disc brakes
have been adopted for front wheels to provide more stable
braking and better braking feel.
3. For some models, a tandem brake booster has been
adopted which provides powerful braking with a light foot
pressure.
4.
For some models, drum-in-disc brakes have been adopted
for rear wheels. This type of brakes have built-in parking
brakes which provide outstanding braking stability.
Improved
serviceability
Higher safety
1.
For ease of inspection, a self-diagnosis capability has been
adopted for the 4ABS.
2. Both the front and rear brakes use a lug nut mounted
outer disc design for ease of removal and installation
3. The master cylinder reserve tank cap is white for easy
recognition
1. An audible wear indicator alerts the driver to the brake
pad limit.
2.
Proportioning valves prevent the rear wheels from locking
too quickly
3. Front and rear X brake lines.
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM