Mitsubishi 380. Manual - part 226
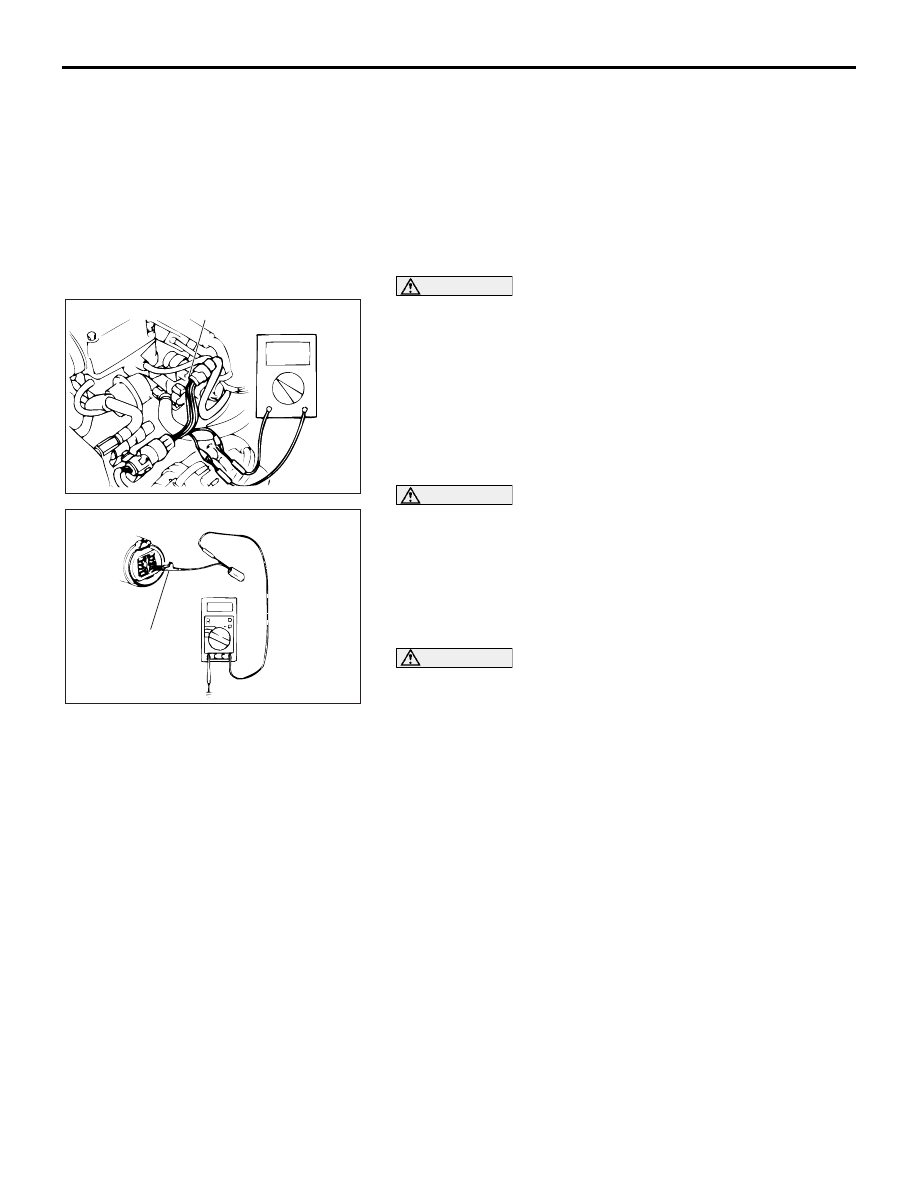
HARNESS CONNECTOR INSPECTION
GENERAL <ELECTRICAL>
00E-2
HARNESS CONNECTOR INSPECTION
M1001003900201
CONNECTOR CONTINUITY AND VOLTAGE TEST
Required Special Tools:
• MB991219: Test Harness Set
• MD998459: Test Harness
Follow the steps below to avoid causing poor connector contact
and/or reduced waterproof performance of connectors when
checking continuity and/or voltage at waterproof connectors.
CAUTION
Never backtest probe a waterproof connector. Backprob-
ing a connector may cause the terminals to corrode, dete-
riorating circuit performance.
1. If the circuit to be checked is a closed state, use a special
tool like MD998459.
CAUTION
Forcing the test probe into the terminal may open the ter-
minal, causing intermittent or poor contact and creating an
open circuit.
2. If the connector is disconnected for checking and the facing
part is the female pin side, use an appropriate male terminal
for checking the contact pressure of connector pins (like
MB991219).
CAUTION
Do not simultaneously contact more than one terminal
with the test probe. Contacting two or more terminals at
the same time may damage a circuit, possibly to the point
of starting an electrical fire.
3. If the facing part is the male pin side, either carefully touch
the test probe to the pin so it does not accidently contact
other pins, or use an appropriate female terminal.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE
HOW TO DIAGNOSE
M1001004300086
The most important point in troubleshooting is to
determine "Probable Cause." Once the probable
causes are determined, parts to be checked can be
limited to those associated with such probable
causes. The determination of the probable causes
must be based on a theory and be supported by facts
and must not be based on intuition only.
AC000014
AB
MD998459
AC000015
AB
MB991219