Jaguar AJV8 engine / 5HP24 transmission. Manual - part 15
AJ-V8/5HP24
61
Engine Management
Variable Valve Timing
The ECM energizes the valve timing solenoids to
advance the intake valve timing and de-energizes
them to retard it.
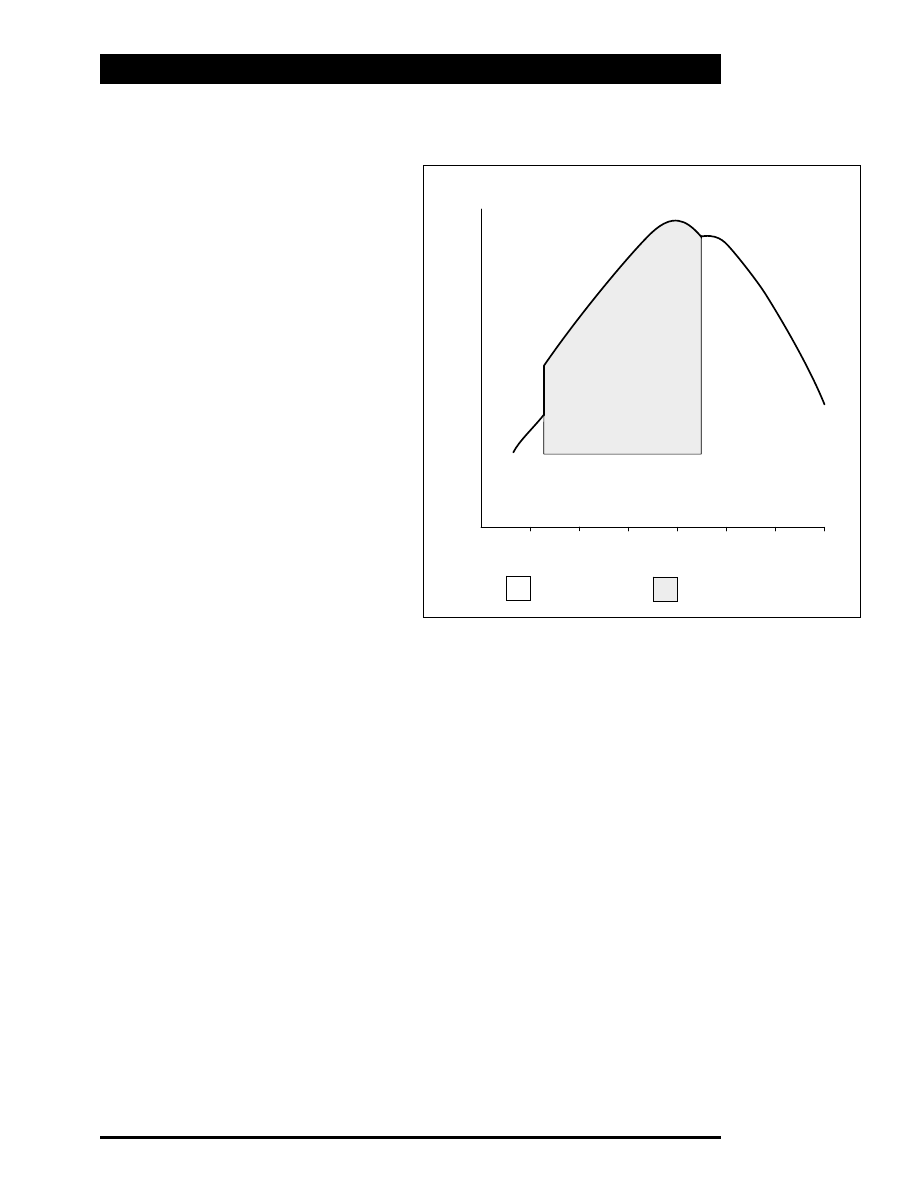
The ECM uses engine load and speed maps to
decide when to advance and retard the timing.
The maps incorporate hysteresis for both engine
load and speed to prevent "hunting".
Between 1250 and 4500 RPM (nominal), at
engine loads greater than approximately 25 % of
the maximum, the timing is advanced. At low
engine loads and at the two ends of the RPM
range, the timing is retarded.
System operation is inhibited at engine coolant
temperatures below -10˚C (14˚F). System
operation is monitored using the input from the
camshaft position sensor. If a fault is detected
the ECM defaults to the retarded (de-energized)
condition.
EGR System
The ECM operates the 4 pole stepper motor in
the EGR valve to control the recirculation of
exhaust gases. Unlike previous systems, there
are no temperature or position feedback signals
from the valve. The ECM monitors EGR operation
using changes of mass air flow.
Engine Starting
At ignition on, if the gear selector is in Park or
Neutral, the ECM enables the fuel injection and
ignition functions. It also outputs a hard wired
digital security acknowledge signal to the BPM to
enable engine cranking. While the engine cranks,
the BPM outputs a hard wired digital engine
cranking signal to the ECM, which employs
engine starting strategies for the duration of the
signal.
If the gear selector is not in Park or Neutral at
ignition on, the ECM inhibits the fuel injection and
ignition functions, and withholds the security
acknowledge signal to prevent cranking.
VARIABLE VALVE TIMING MAP
Engine Speed, RPM x 1000
Retarded
Advanced
Engine Load
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
303-135