Isuzu Rodeo UE. Manual - part 264
6E1–427
RODEO X22SE 2.2L ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSION
lower oxygen sensor response. This may cause incorrect
catalyst monitor diagnostic results.
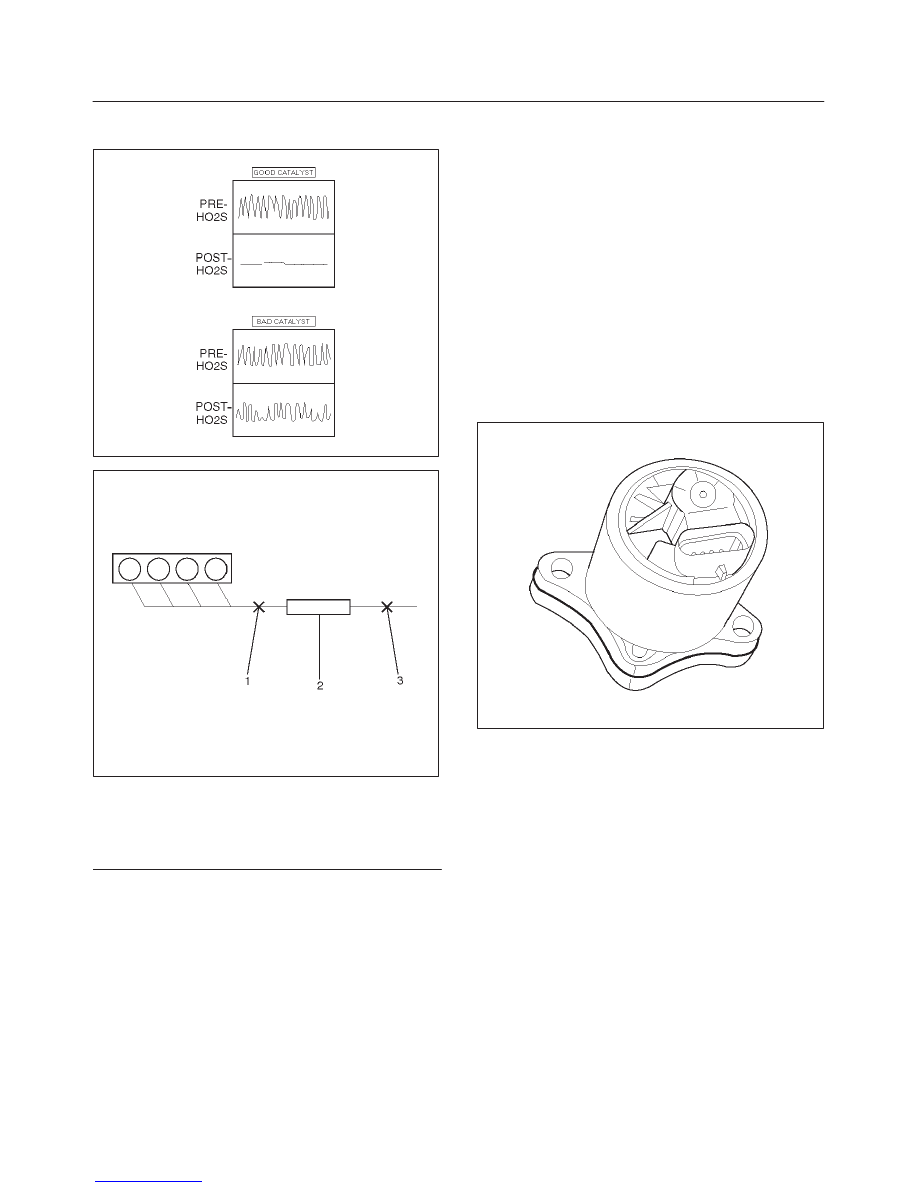
TS24067
D06RX025
Legend
(1) Bank 1 Sensor 1 (Fuel Control)
(2) Catalytic Converter
(3) Bank 1 Sensor 2 (Catalyst Monitor)
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which changes its resistance based on the temperature of
air entering the engine. Low temperature produces a high
resistance of about 100,000
W
at –40
°
C (–104
°
F). High
temperature causes low resistance of about 70
W
at
130
°
C (266
°
F). The PCM supplies a 5–volt signal to the
sensor through a resistor internal to the PCM, and then
monitors the signal voltage. The voltage will be high when
the incoming air is cold. The voltage will be low when the
incoming air is hot. By measuring the voltage, the PCM
calculates the incoming air temperature. The IAT sensor
signal is used to adjust spark timing according to the
incoming air density.
The Tech 2 displays the temperature of the air entering
the engine. The temperature should read close to the
ambient air temperature when the engine is cold and rise
as underhood temperature increases. If the engine has
not been run for several hours (overnight), the IAT sensor
temperature and engine coolant temperature should read
close to each other. A failure in the IAT sensor circuit will
set DTC P0112, DTC P1111, DTC P1112, or DTC P0113.
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Control
The PCM monitors the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
actual position and adjusts the pintle position accordingly.
The PCM uses information from the following sensors to
control the pintle position:
f
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
f
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
f
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
0017
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the PCM varies from below
2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above 4 volts with the
ignition ON, engine not running or at wide–open throttle
(low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine the following:
f
Manifold pressure changes while the linear EGR flow
test diagnostic is being run. Refer to DTC P0401.
f
Engine vacuum level for other diagnostics.
f
Barometric pressure (BARO).
If the PCM detects a voltage that is lower than the
possible range of the MAP sensor, DTC P0107 will be set.
A signal voltage higher than the possible range of the
sensor will set DTC P0108. An intermittent low or high
voltage will set DTC P1107 or P1106, respectively. The
PCM can detect a shifted MAP sensor. The PCM
compares the MAP sensor signal to a calculated MAP
based on throttle position and various engine load factors.
If the PCM detects a MAP signal that varies excessively
above or below the calculated value, DTC P0106 will set.