Dodge Dakota (R1). Manual - part 810
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE - EVAP SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
N·m
Ft. Lbs.
In. Lbs.
EVAP Canister Mounting Nut
17-24
150-210
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid Mounting Bolt – Except 2.5L
Engine
11
95
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid Mounting Nuts – 2.5L Engine
8
75
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Mounting Screws
1
11
CCV HOSE
DESCRIPTION - 2.5L
2.5L 4–cylinder engines are equipped with a
Crankcase Ventilation (CCV) system. The CCV sys-
tem performs the same function as a conventional
PCV system, but does not use a vacuum controlled
valve.
A molded vacuum tube connects a fitting on the
intake manifold to a fixed orifice fitting of a cali-
brated size. This fitting meters the amount of crank-
case vapors drawn out of the engine. The fixed orifice
fitting is located on the side of cylinder head (valve)
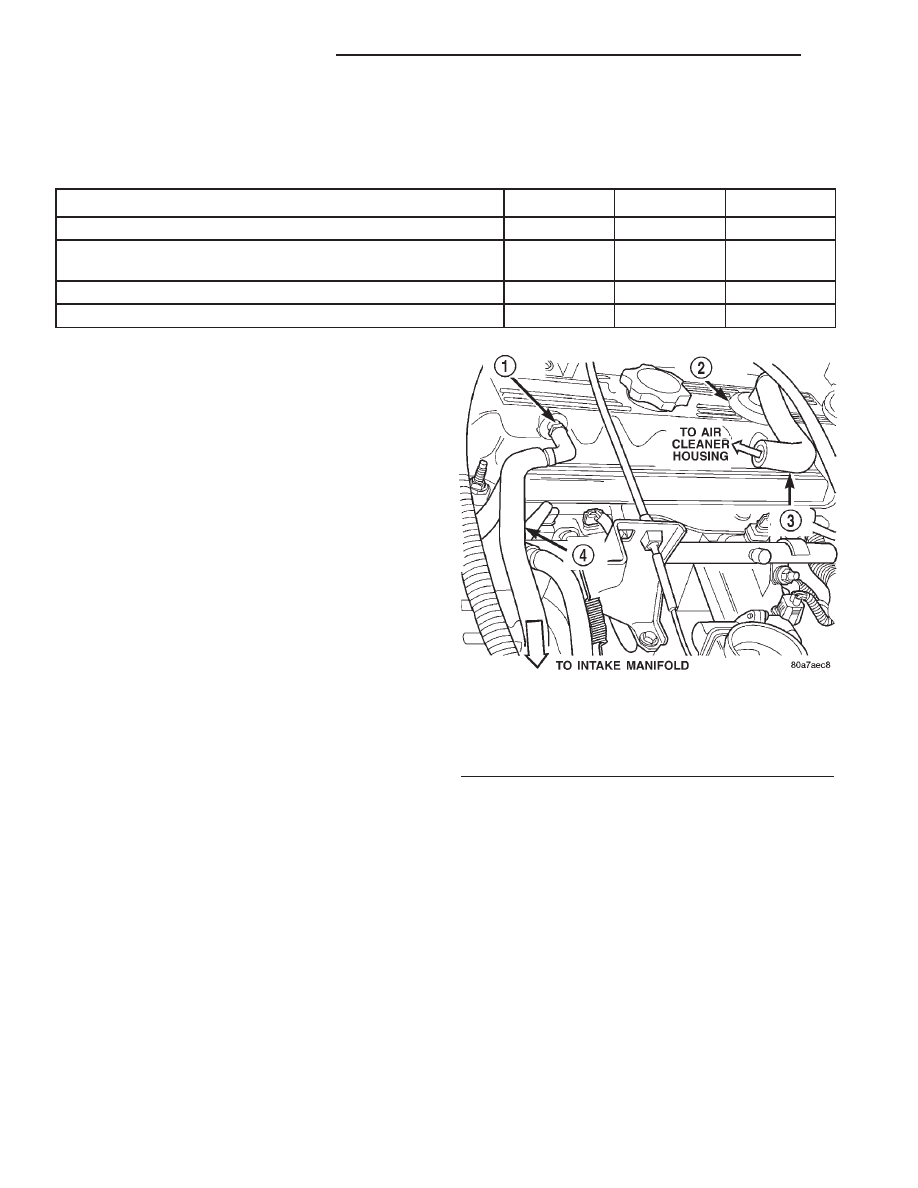
cover (Fig. 1).
A fresh air supply hose from the air cleaner hous-
ing is connected to a fitting at the top/rear of cylinder
head cover (Fig. 1).
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Engine vac-
uum draws the vapor/air mixture through the fixed
orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors are
then consumed during engine combustion.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
3.9/5.2/5.9L Engines: The duty cycle EVAP canister
purge solenoid is located at left-rear side of engine com-
partment near power brake vacuum unit (Fig. 2).
2.5L Engine: The solenoid is located at right-rear
side of engine compartment (Fig. 3).
(1) Disconnect electrical wiring connector at solenoid
(2) Disconnect vacuum harness at solenoid.
(3) Remove 2 support bracket mounting nuts.
(4) Remove solenoid and its support bracket from
vehicle.
Fig. 1 CCV System—2.5L Engine
1 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
2 - AIR INLET FITTING
3 - CCV TUBE
4 - CCV TUBE
25 - 24
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
AN
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)