Chrysler RG Voyager. Manual - part 924
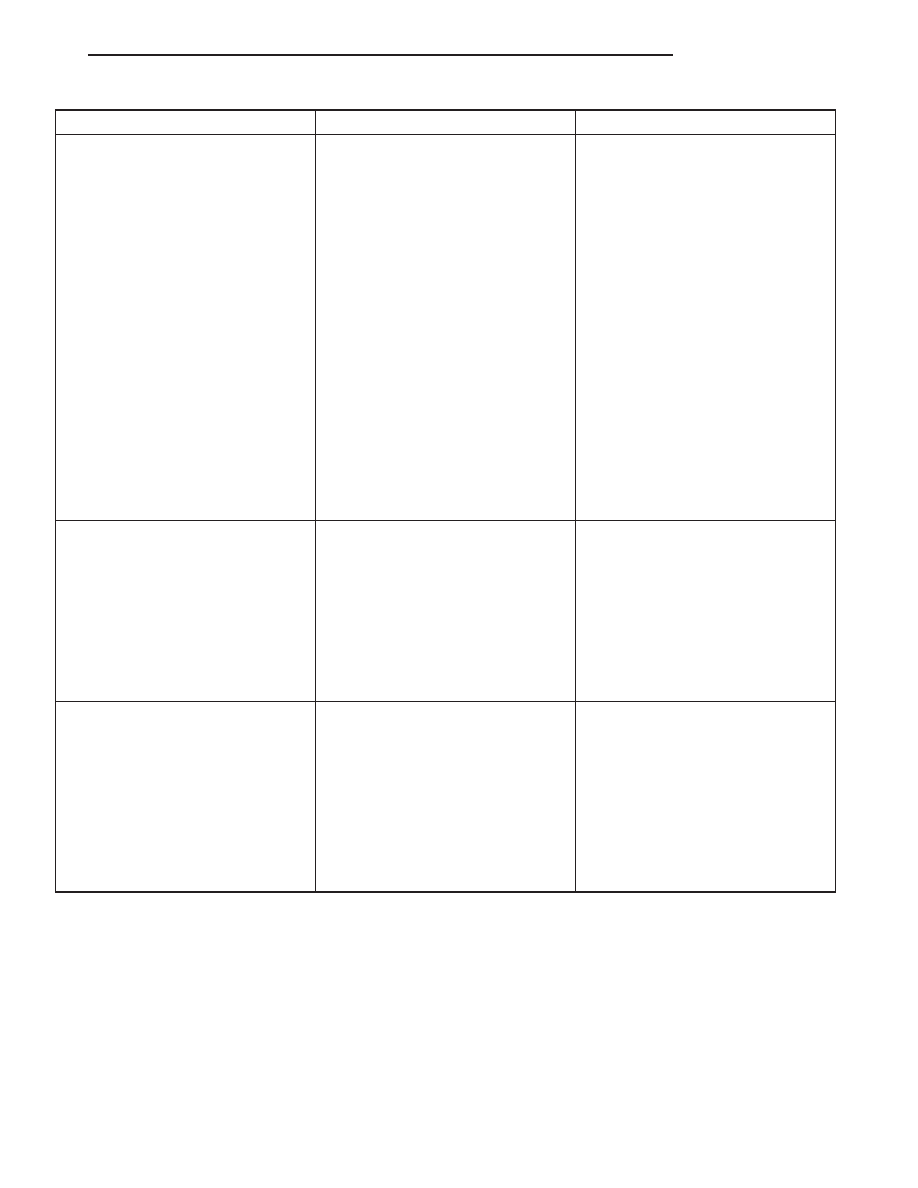
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSE
CORRECTION
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER
1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs.
1. Clean plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in fuel system.
2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump.
3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Incorrect valve timing.
4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket.
5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression.
6. Test compression of each
cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves.
7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.
8. Perform exhaust restriction test.
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) Install
new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition coil(s).
9. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION
1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.
1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in Fuel System.
2. Clean fuel system and replace
fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves.
3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s).
4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED
1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap.
1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Faulty ignition coil(s).
2. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Dirty fuel injector(s).
3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Contamination in fuel system.
4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
RS
ENGINE 2.4L
9 - 5
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)