Suzuki Grand Vitara JB416 / JB420. Manual - part 111
1D-112 Engine Mechanical: For J20 Engine
4) Install piston pin to piston (1) and connecting rod (3):
After applying engine oil to piston pin and piston pin
holes in piston and connecting rod, fit connecting rod
to piston as shown in figure and insert piston pin to
piston and connecting rod, and install piston pin
circlips.
NOTE
Oil hole (4) come on intake side.
NOTE
Circlip (4) should be installed so that circlip
end gap comes within such range as
indicated by arrow.
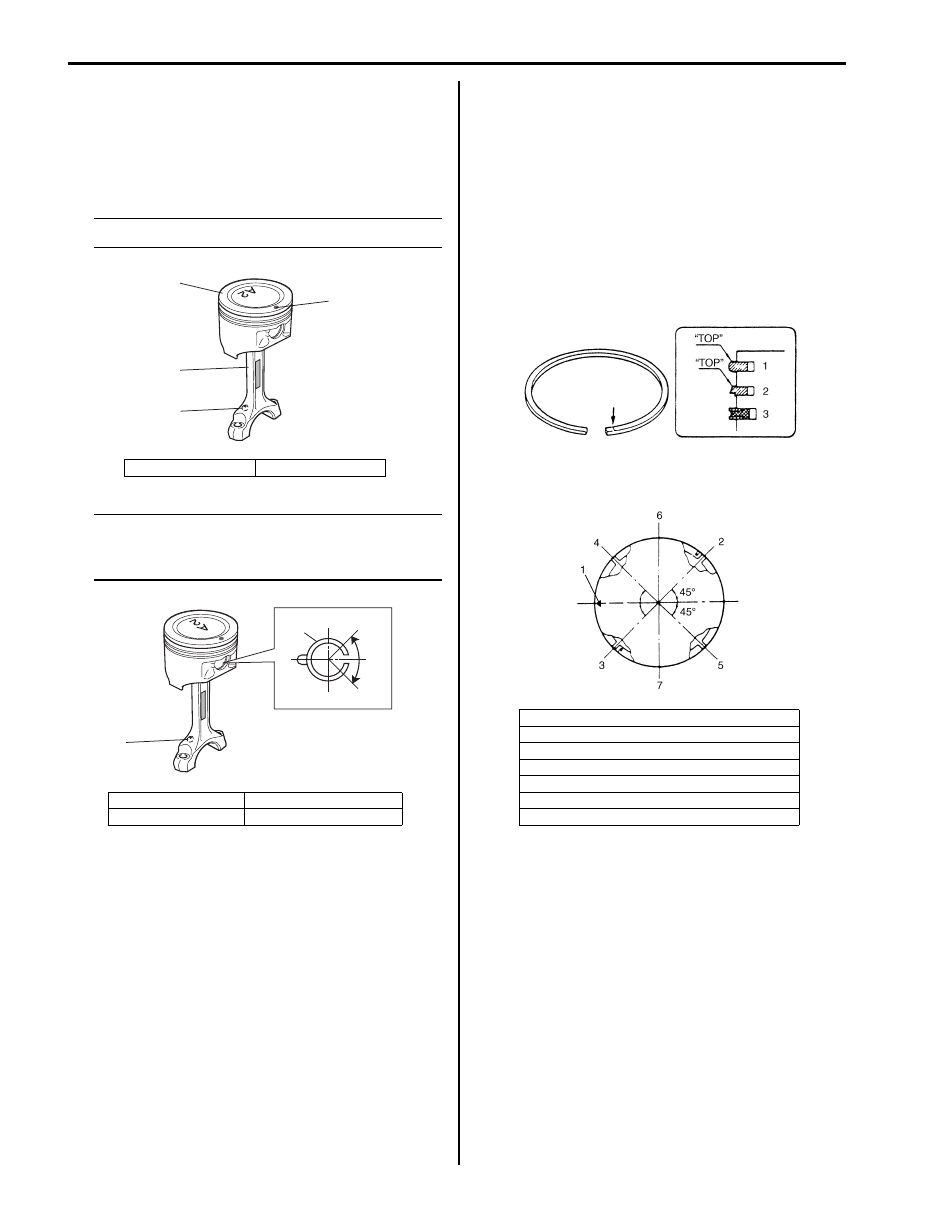
5) Install piston rings to piston:
• As indicated in figure at the left, 1st and 2nd rings
have “TOP” mark respectively. When installing
these piston rings to piston, direct marked side of
each ring toward top of piston.
• 1st ring (1) differs from 2nd ring (2) in thickness,
shape and color of surface contacting cylinder
wall.
Distinguish 1st ring from 2nd ring by referring to
figure.
• When installing oil ring (3), install spacer first and
then two rails.
6) After installing three rings (1st, 2nd and oil rings),
distribute their end gaps as shown in figure.
2. Front mark
4. Oil hole
1. Piston
3. Connecting rod
2. Front mark
5. Oil hole
1
2
3
4
I5JB0A142051-01
4
5
I4RH01140039-01
1. Front mark
2. 1st ring end gap
3. 2nd ring end gap and oil ring spacer gap
4. Oil ring upper rail gap
5. Oil ring lower rail gap
6. Intake side
7. Exhaust side
I5JB0A142052-02
I5JB0A142053-01