Content .. 1167 1168 1169 1170 ..
Nissan Teana J32. Manual - part 1169
TM-200
< FUNCTION DIAGNOSIS >
[CVT: RE0F10A]
SHIFT LOCK SYSTEM
SHIFT LOCK SYSTEM
System Description
INFOID:0000000003806370
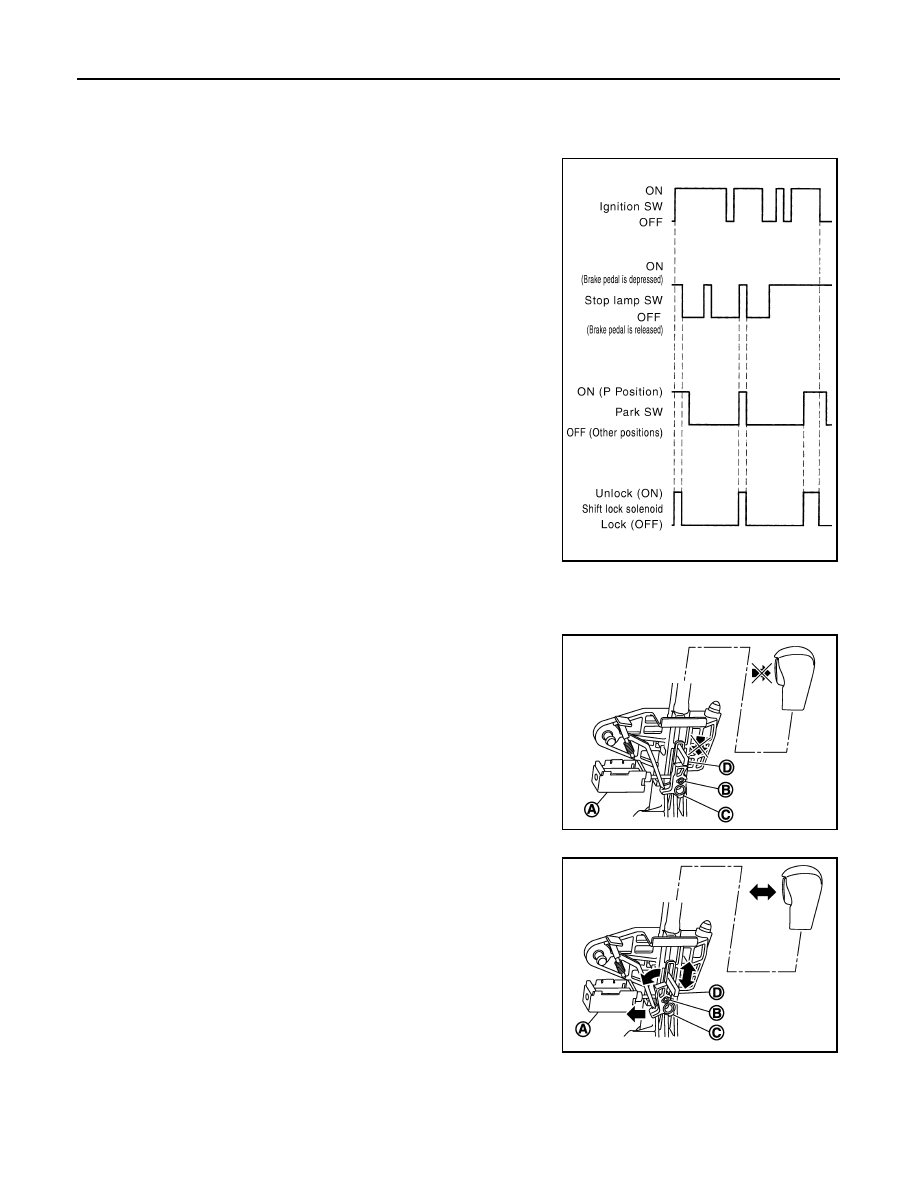
The shift lever it cannot be shifted from the “P” position unless the
brake pedal is depressed while the ignition switch is set to ON. The
shift lock is unlocked by turning the shift lock solenoid ON when the
ignition switch is set to ON, the park switch is turned ON (selector
lever is in “P” position), and the stop lamp switch is turned ON (brake
pedal is depressed) as shown in the operation chart in the figure.
Therefore, the shift lock solenoid receives no ON signal and the shift
lock remains locked if all of the above conditions are not fulfilled.
(However, selector operation is allowed if the shift lock release but-
ton is pressed.)
SHIFT LOCK OPERATION at “P” POSITION
When Brake Pedal Is Not Depressed (No Selector Operation Allowed)
The shift lock solenoid (A) is turned OFF (not energized) and the
solenoid rod (B) is extended with the spring when the brake pedal is
not depressed (no selector operation allowed) with the ignition
switch ON.
The connecting lock lever (C) is located at the position shown in the
figure when the solenoid rod is extended. It prevents the movement
of the detent rod (D). The selector lever cannot be shifted from the P
position for this reason.
When Brake Pedal Is Depressed (Shift Operation Allowed)
The shift lock solenoid (A) is turned ON (energized) when the brake
pedal is depressed with the ignition switch ON. The solenoid rod (B)
is compressed by the electromagnetic force. The connecting lock
lever (C) rotates when the solenoid rod is activated. Therefore, the
detent rod (D) can be moved. The selector lever can be shifted to
other positions for this reason.
“P” POSITION HOLD MECHANISM (IGNITION SWITCH LOCK)
JPDIA0588GB
JPDIA0612ZZ
JPDIA0613ZZ