Mitsubishi Pajero Pinin. Manual - part 235
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM –
On-vehicle Service
35A-8
3.
With the engine running, step on the brake pedal and
then stop the engine.
Hold the pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If the pedal
height does not change, the booster is in good condition.
If the pedal rises, the booster is defective.
If the above three tests are okay, the booster performance
can be determined as good.
If one of the above three tests is not okay at least, the check
valve, vacuum hose, or booster will be defective.
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECK
1.
Remove the vacuum hose. (Refer to P.35A-15, 16.)
Caution
The check valve should not be disassembled from
the vacuum hose as they are united as one part.
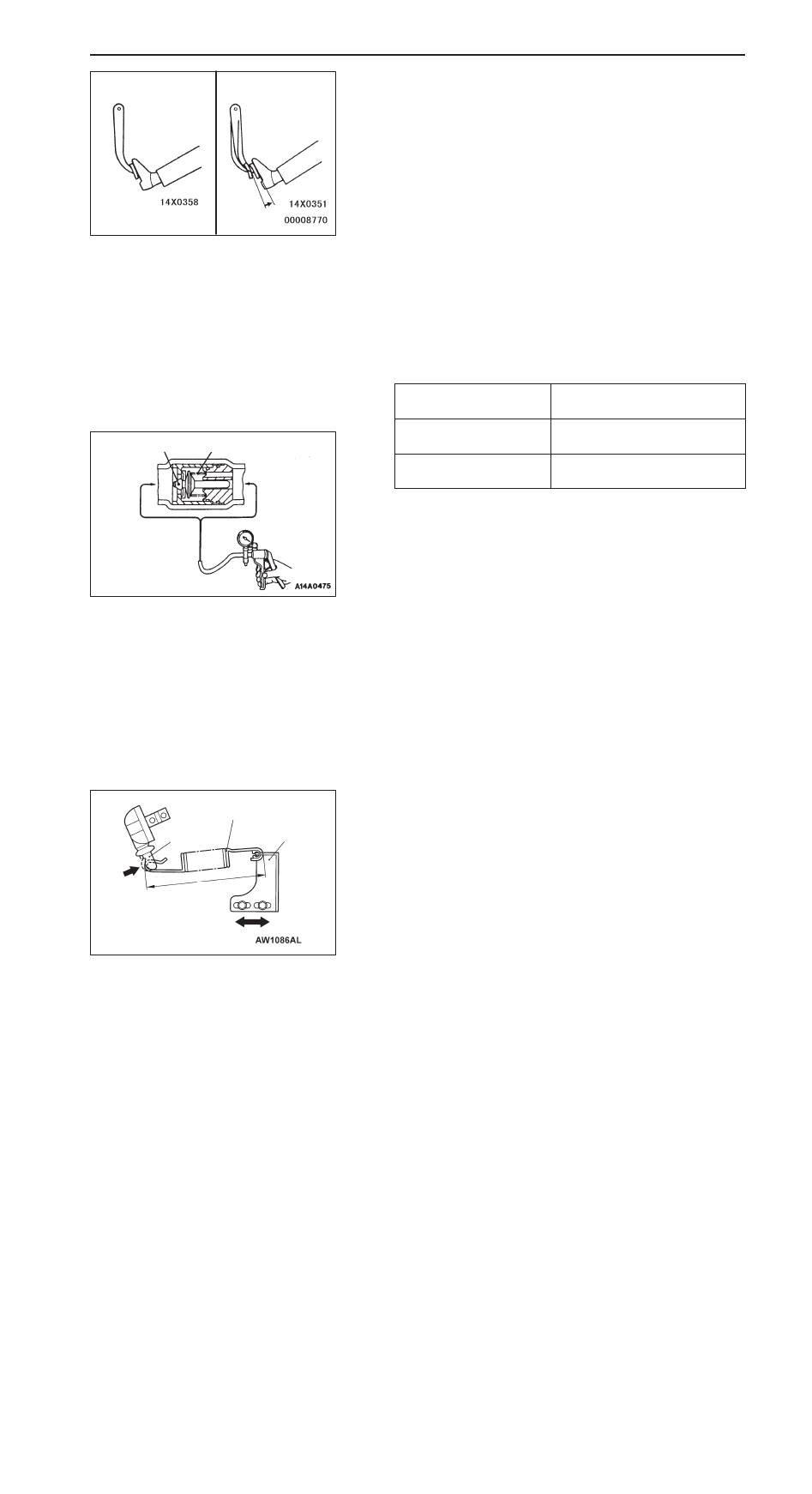
2.
Check the operation of the check valve by using a vacuum
pump.
Vacuum pump
connection
Accept/reject criteria
Connection at the brake
booster side (A)
A negative pressure (vacuum) is
created and held.
Connection at the intake
manifold side (B)
A negative pressure (vacuum) is
not created.
Caution
If the check valve is defective, always replace it as
an assembly unit together with the vacuum hose.
LOAD SENSING SPRING LENGTH CHECK
AND ADJUSTMENT
1.
Park the vehicle on a level ground. The vehicle should
be unloaded and supported only by wheels.
Caution
Never support the vehicle with jacks or other similar
means.
2.
With the lever pressed all the way to the load sensing
proportioning valve side, check whether or not the length
(shown in the figure) of the spring (the length between
its ends) is the standard value.
Standard value (A): 194 – 198 mm
3.
If the spring length is not within the standard value, loosen
the bolt attaching the support and adjust the distance by
moving the support.
Good
No good
Valve
Spring
Booster
side
A
B
Intake
manifold
side
Load sensing spring
Spring support
Lever
A