Iveco Daily. Manual - part 393
Four parallel channel system (II)
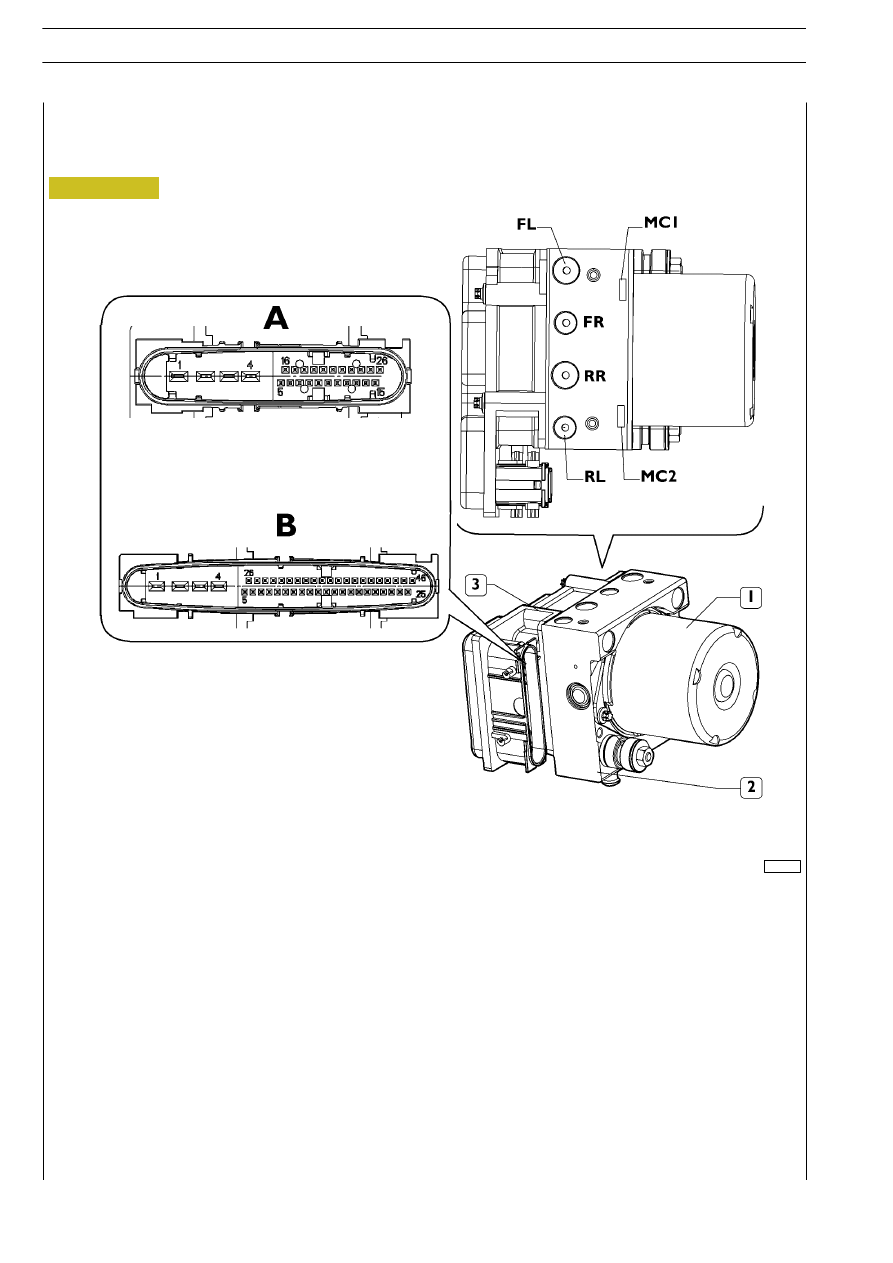
Electro-hydraulic modulator/control unit
1. Hydraulic accumulator
-- 2. Electro-hydraulic modulator -- 3. Electronic control unit -- A. ABS8 connector -- B. ESP8
connector
-- MC1. Front axle power supply -- MC2. Rear axle power supply -- LF (or FL with ABS8/ESP8 systems). Left front
axle output
-- RR. Right rear axle output -- RF (or FR with ABS8/ESP8 systems). Right front axle output -- LR (or RL with
ABS8/ESP8 systems). Left rear axle output
102114
Figure 131/2
132/4
ELECTRIC/ELECTRONIC SYSTEM
D
AILY
Revi - February 2005