Isuzu engine C22NE / 22LE / 20LE. Manual - part 114
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E1-285
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ECM AND SENSORS
58X REFERENCE ECM INPUT
The engine control module (ECM) uses this signal from the
crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to calculate engine RPM and
crankshaft position at all engine speeds. The ECM also uses
the pulses on this circuit to initiate injector pulses. If the ECM
receives a number of pulses other than the expected amount,
DTC 19, will set. The engine will not start and run without using
the 58X reference signal.
A/C REQUEST SIGNAL
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected at the
A/C control switch. The ECM uses this signal to adjust the idle
speed before turning ON the A/C clutch. The A/C compressor
will be inoperative if this signal is not available to the ECM.
Refer to A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring diagrams
and diagnosis for the A/C electrical system.
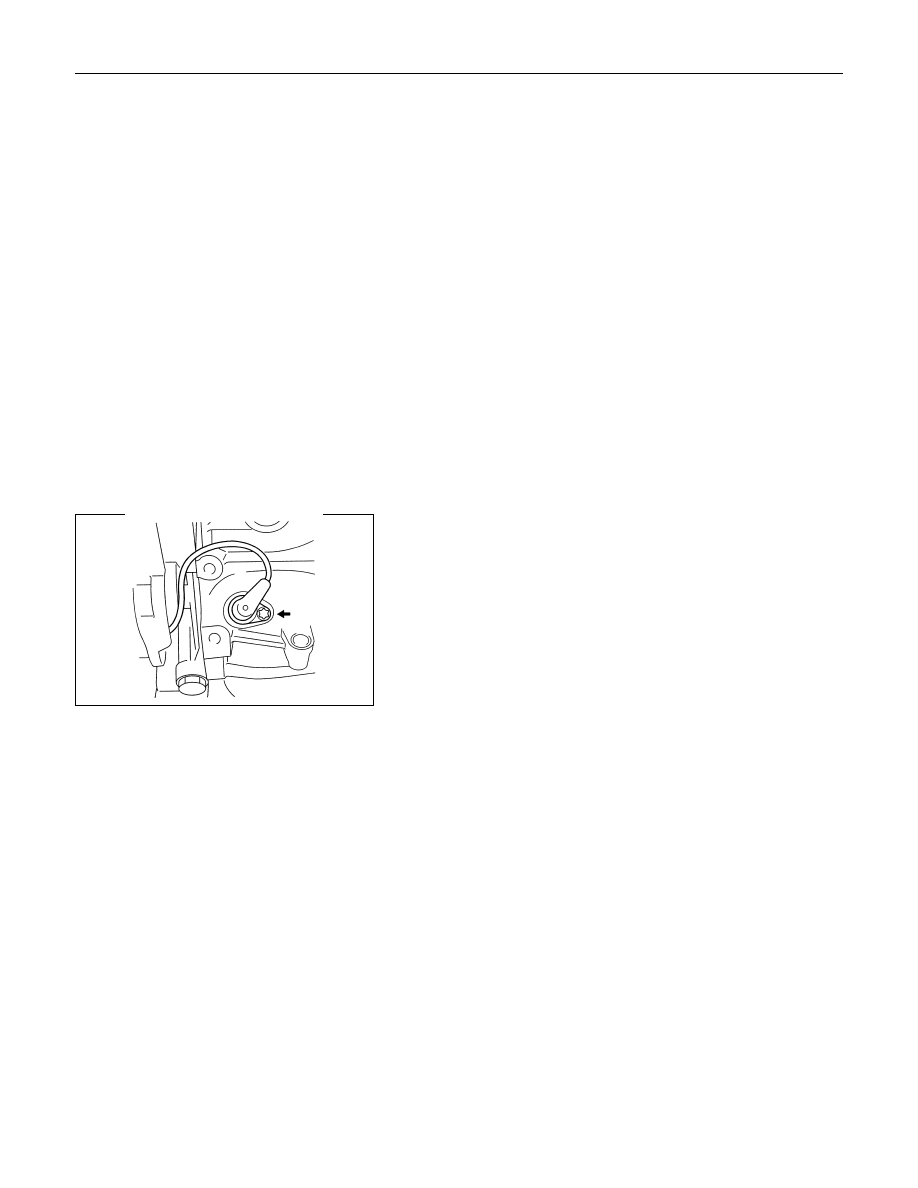
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor provides a signal used
by the engine control module (ECM) to calculate the ignition
sequence and ECM uses this signal as a trigger for fuel
injection timing and spark timing. The CKP sensor initiates the
58X reference pulses which the ECM uses to calculate RPM
and crankshaft position.
Refer to Electronic Ignition System for additional information.