Isuzu Rodeo UE. Manual - part 181
6E1–95
RODEO X22SE 2.2L ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSION
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) SYSTEM CHECK
D06RX041
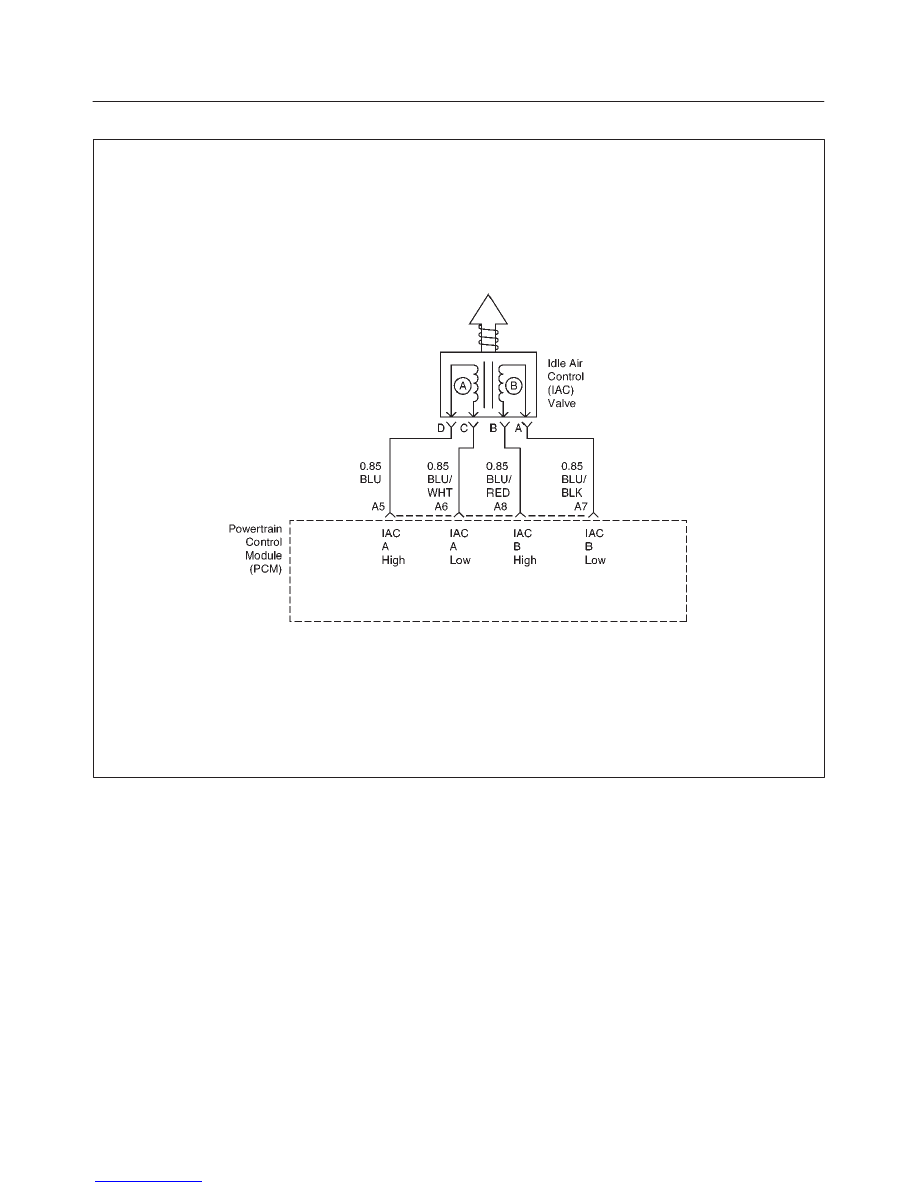
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls engine
idle speed with the idle air control (IAC) valve. To increase
idle speed, the PCM retracts the IAC valve pintle away
from its seat, allowing more air to bypass the throttle bore.
To decrease idle speed, it extends the IAC valve pintle
towards its seat, reducing bypass air flow. A Tech 2 will
read the PCM commands to the IAC valve in counts.
Higher counts indicate more air bypass (higher idle).
Lower counts indicate less air is allowed to bypass (lower
idle).
Diagnostic Aids
A slow, unstable, or fast idle may be caused by a non–IAC
system problem that cannot be overcome by the IAC
valve. Out of control range IAC Tech 2 counts will be
above 60 if idle is too low, and zero counts if idle is too
high. The following checks should be made to repair a
non–IAC system problem:
f
Vacuum leak (high idle) – If idle is too high, stop the
engine. Fully extend (low) IAC with the IAC motor
analyzer J 39027–A. Start the engine. If idle speed is
above 800 RPM, locate and correct the vacuum leak,
including the PCV system. Check for binding of the
throttle blade or linkage.
f
Lean heated oxygen sensor signal (high air/fuel ratio)
– The idle speed may be too high or too low. Engine
speed may vary up and down, and disconnecting the
IAC valve does not help. Diagnostic trouble codes
P0131, P0151, P0171, or P0174 may be set. Tech 2
oxygen (O2) voltage will be less than 100 mV (0.1 V).
Check for low regulated fuel pressure, water in fuel, or
a restricted injector.